Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework designed to manage, store, and process extensive data sets for various big data applications within clustered systems. It is primarily written in Java, with some components in C and shell scripts. Hadoop leverages a distributed file system (HDFS) that can scale from single servers to thousands of machines.
Apache Hadoop comprises four main components:
- Hadoop Common: A collection of utilities and libraries essential for other Hadoop modules.
- HDFS: Hadoop Distributed File System, spread across multiple nodes.
- MapReduce: A framework for writing applications to process massive volumes of data.
- Hadoop YARN: Stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator, serving as the resource management layer of Hadoop.
This guide will show you how to set up a single-node Hadoop cluster on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 20.04 with at least 4 GB of RAM.
- A configured root password on your server.
Update System Packages
It’s advisable to update your system packages to the latest versions before you begin. Use the commands below:
apt-get update -y apt-get upgrade -y
Once the system is updated, restart it to apply the changes.
Install Java
Since Apache Hadoop is Java-based, you’ll need to install Java. Execute the following command:
apt-get install default-jdk default-jre -y
Verify the Java installation with:
java -version
Expected output:
openjdk version "11.0.7" 2020-04-14 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.7+10-post-Ubuntu-3ubuntu1, mixed mode, sharing)
Create Hadoop User and Set Up Passwordless SSH
Create a user named hadoop with the command:
adduser hadoop
Add the hadoop user to the sudo group:
usermod -aG sudo hadoop
Switch to the hadoop user and generate an SSH key pair:
su - hadoop ssh-keygen -t rsa
Expected output:
Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/hadoop/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/home/hadoop/.ssh'. Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/hadoop/.ssh/id_rsa Your public key has been saved in /home/hadoop/.ssh/id_rsa.pub The key fingerprint is: SHA256:HG2K6x1aCGuJMqRKJb+GKIDRdKCd8LXnGsB7WSxApno hadoop@ubuntu2004 The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 3072]----+ |..=.. | | O.+.o . | |oo*.o + . o | |o .o * o + | |o+E.= o S | |=.+o * o | |*.o.= o o | |=+ o.. + . | |o .. o . | +----[SHA256]-----+
Append the public key to the authorized keys and set proper permissions:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys chmod 0600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Verify passwordless SSH access:
ssh localhost
Once passwordless login is confirmed, continue to the next step.
Install Hadoop
Log in as hadoop and download the latest Hadoop version:
su - hadoop wget https://downloads.apache.org/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.2.1/hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz
Extract the download:
tar -xvzf hadoop-3.2.1.tar.gz
Move the directory to /usr/local/:
sudo mv hadoop-3.2.1 /usr/local/hadoop
Create a directory for logs:
sudo mkdir /usr/local/hadoop/logs
Change ownership of the Hadoop directory:
sudo chown -R hadoop:hadoop /usr/local/hadoop
Set up Hadoop environment variables by editing ~/.bashrc:
nano ~/.bashrc
Add:
export HADOOP_HOME=/usr/local/hadoop export HADOOP_INSTALL=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/sbin:$HADOOP_HOME/bin export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=$HADOOP_HOME/lib/native"
Save and activate the variables:
source ~/.bashrc
Configure Hadoop
Set up Hadoop for single-node use.
Configure Java Environment Variables
Define Java path in hadoop-env.sh for YARN, HDFS, and MapReduce configurations.
Locate the Java path:
which javac
Expected output:
/usr/bin/javac
Find the OpenJDK directory:
readlink -f /usr/bin/javac
Expected output:
/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javac
Edit hadoop-env.sh to define the Java path:
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
Add:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64 export HADOOP_CLASSPATH+=" $HADOOP_HOME/lib/*.jar"
Download the Javax activation file:
cd /usr/local/hadoop/lib sudo wget https://jcenter.bintray.com/javax/activation/javax.activation-api/1.2.0/javax.activation-api-1.2.0.jar
Verify the Hadoop version:
hadoop version
Expected output:
Hadoop 3.2.1 Source code repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/hadoop.git -r b3cbbb467e22ea829b3808f4b7b01d07e0bf3842 Compiled by rohithsharmaks on 2019-09-10T15:56Z Compiled with protoc 2.5.0 From source with checksum 776eaf9eee9c0ffc370bcbc1888737 This command was run using /usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-common-3.2.1.jar
Configure core-site.xml File
Edit core-site.xml to specify the URL for your NameNode:
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
Add:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.default.name</name>
<value>hdfs://0.0.0.0:9000</value>
<description>The default file system URI</description>
</property>
</configuration>
Save and exit the file.
Configure hdfs-site.xml File
Define metadata storage locations in hdfs-site.xml.
Create metadata directories:
sudo mkdir -p /home/hadoop/hdfs/{namenode,datanode}
sudo chown -R hadoop:hadoop /home/hadoop/hdfs
Edit hdfs-site.xml:
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
Add:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.replication</name>
<value>1</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.name.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hdfs/namenode</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.data.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hdfs/datanode</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Save and close the file.
Configure the mapred-site.xml File
Set MapReduce values in mapred-site.xml:
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
Add:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>mapreduce.framework.name</name>
<value>yarn</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Save and close the file.
Configure yarn-site.xml File
Edit yarn-site.xml to define YARN configurations:
sudo nano $HADOOP_HOME/etc/hadoop/yarn-site.xml
Add:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>yarn.nodemanager.aux-services</name>
<value>mapreduce_shuffle</value>
</property>
</configuration>
Save and exit the file.
Format HDFS NameNode
Verify Hadoop configuration and format the HDFS NameNode.
Log in as hadoop and format the NameNode:
su - hadoop hdfs namenode -format
Expected output:
2020-06-07 11:35:57,691 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 2020-06-07 11:35:57,692 INFO util.GSet: 0.25% max memory 1.9 GB = 5.0 MB 2020-06-07 11:35:57,692 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^19 = 524288 entries 2020-06-07 11:35:57,706 INFO metrics.TopMetrics: NNTop conf: dfs.namenode.top.window.num.buckets = 10 2020-06-07 11:35:57,706 INFO metrics.TopMetrics: NNTop conf: dfs.namenode.top.num.users = 10 2020-06-07 11:35:57,706 INFO metrics.TopMetrics: NNTop conf: dfs.namenode.top.windows.minutes = 1,5,25 2020-06-07 11:35:57,710 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache on namenode is enabled 2020-06-07 11:35:57,710 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache will use 0.03 of total heap and retry cache entry expiry time is 600000 millis 2020-06-07 11:35:57,712 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map NameNodeRetryCache 2020-06-07 11:35:57,712 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 2020-06-07 11:35:57,712 INFO util.GSet: 0.029999999329447746% max memory 1.9 GB = 611.9 KB 2020-06-07 11:35:57,712 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^16 = 65536 entries 2020-06-07 11:35:57,743 INFO namenode.FSImage: Allocated new BlockPoolId: BP-1242120599-69.87.216.36-1591529757733 2020-06-07 11:35:57,763 INFO common.Storage: Storage directory /home/hadoop/hdfs/namenode has been successfully formatted. 2020-06-07 11:35:57,817 INFO namenode.FSImageFormatProtobuf: Saving image file /home/hadoop/hdfs/namenode/current/fsimage.ckpt_0000000000000000000 using no compression 2020-06-07 11:35:57,972 INFO namenode.FSImageFormatProtobuf: Image file /home/hadoop/hdfs/namenode/current/fsimage.ckpt_0000000000000000000 of size 398 bytes saved in 0 seconds . 2020-06-07 11:35:57,987 INFO namenode.NNStorageRetentionManager: Going to retain 1 images with txid >= 0 2020-06-07 11:35:58,000 INFO namenode.FSImage: FSImageSaver clean checkpoint: txid=0 when meet shutdown. 2020-06-07 11:35:58,003 INFO namenode.NameNode: SHUTDOWN_MSG: /************************************************************ SHUTDOWN_MSG: Shutting down NameNode at ubuntu2004/69.87.216.36 ************************************************************/
Start the Hadoop Cluster
Start the NameNode and DataNode using:
start-dfs.sh
Expected output:
Starting namenodes on [0.0.0.0] Starting datanodes Starting secondary namenodes [ubuntu2004]
Start the YARN resource and nodemanagers:
start-yarn.sh
Expected output:
Starting resourcemanager Starting nodemanagers
Verify the processes:
jps
Expected output:
5047 NameNode 5850 Jps 5326 SecondaryNameNode 5151 DataNode
Access Hadoop Web Interface
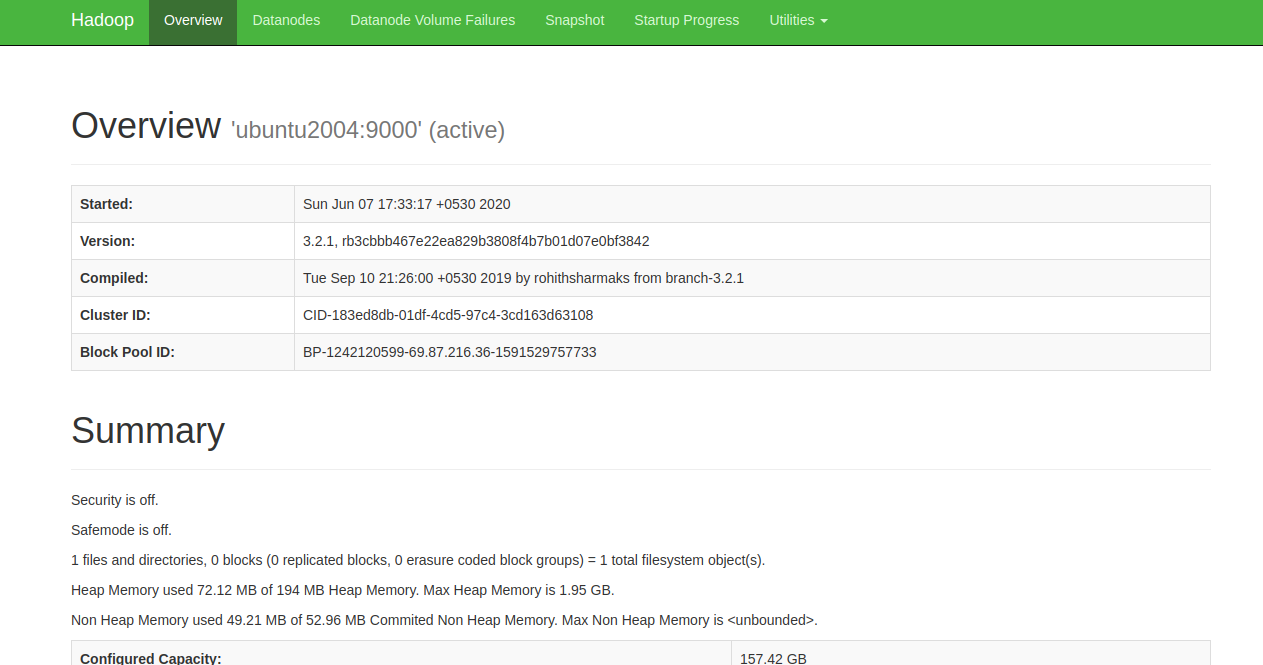
Access the Hadoop NameNode at http://your-server-ip:9870. You should see:
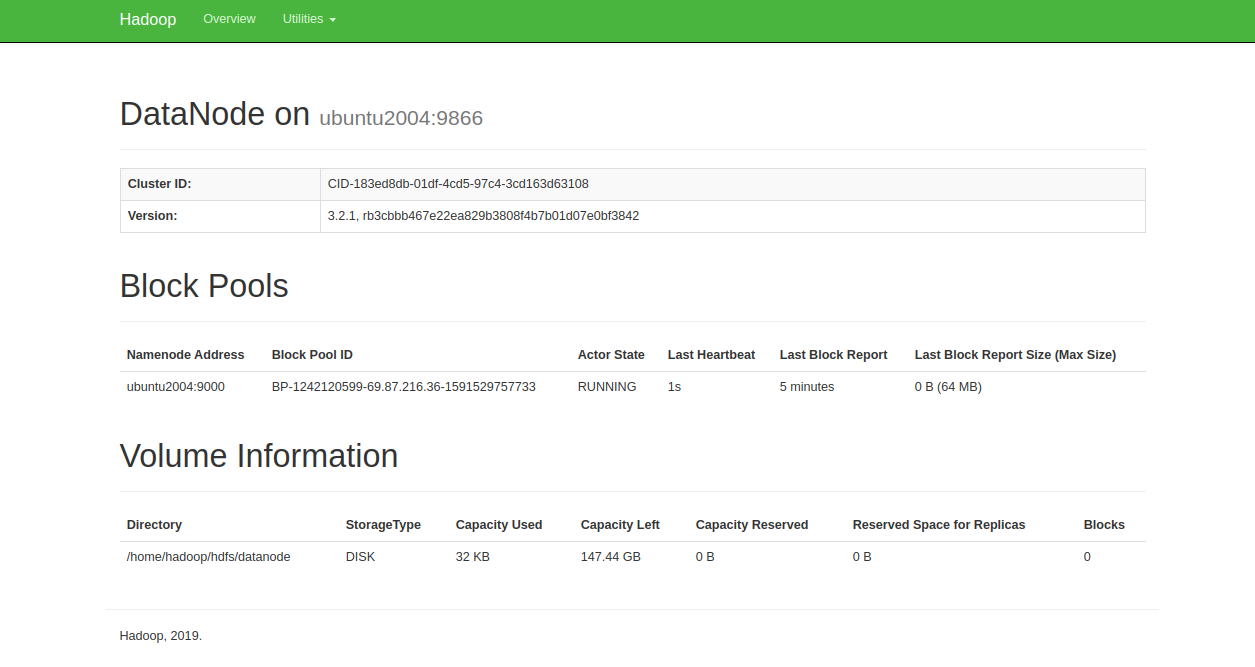
Access individual DataNodes via http://your-server-ip:9864. You should see:
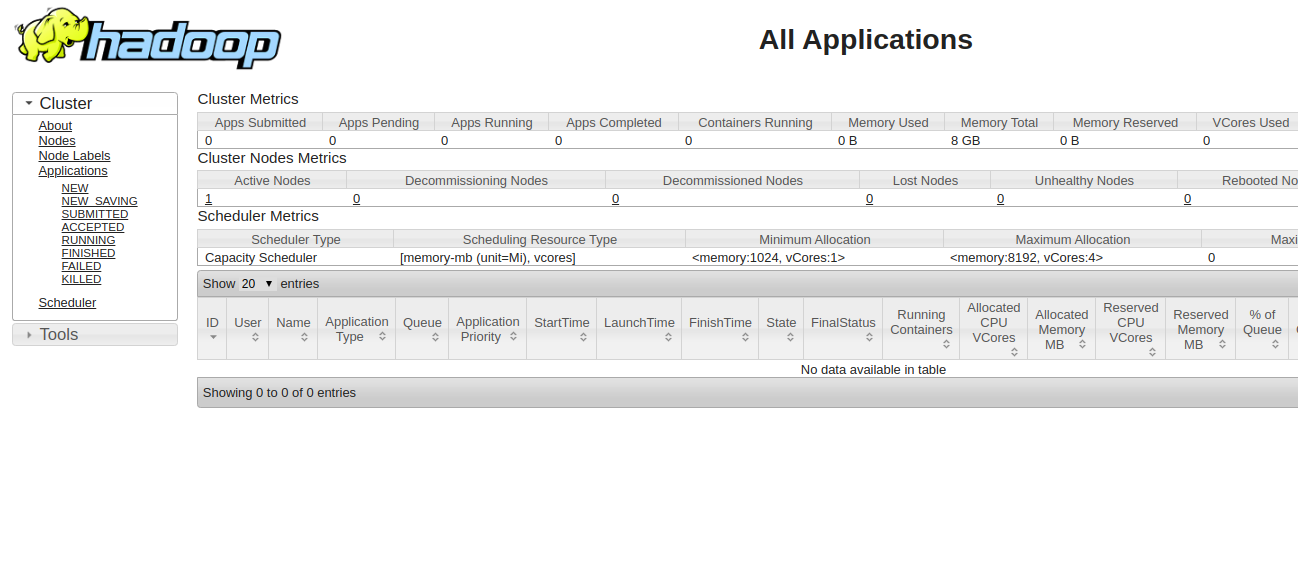
Access the YARN Resource Manager at http://your-server-ip:8088. You should see:
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully set up Hadoop on a single node. You are now ready to explore basic HDFS commands and eventually expand to a fully distributed Hadoop cluster. Feel free to ask me if you have any questions.
FAQs
- Can I use a different Linux distribution for setting up Hadoop?Yes, Hadoop can be installed on various Linux distributions, but package names and installation steps may vary. This guide specifically uses Ubuntu 20.04.
- Is it possible to set up a multi-node Hadoop cluster on the same system?Testing a multi-node setup on a single machine is possible with virtual machines or containerization tools like Docker, but it’s generally intended for lab or educational purposes rather than production.
- What are the storage requirements for Hadoop?Hadoop’s storage needs depend on your data volume. Always plan for more storage than the data volume due to replication requirements (HDFS default is threefold replication).
- How do I stop all running Hadoop services?You can stop all Hadoop services using the commands:
stop-dfs.sh stop-yarn.sh
- Is a single-node Hadoop cluster recommended for production environments?No, single-node clusters are primarily for development and testing. Production environments should consist of multi-node clusters for redundancy and performance.
