OpenVPN is an open-source software allowing secure private network creation over the internet. It implements a robust VPN (Virtual Private Network) solution using the OpenSSL library to ensure encryption and offers diverse authentication mechanisms, including certificate-based authentication, pre-shared keys, and username/password authentication.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the steps to install and configure OpenVPN on CentOS 7.6 with certificate-based authentication.
Prerequisites
- CentOS 7.6
- Root access
Steps to Follow
- Install OpenVPN and Easy-RSA
- Configure Easy-RSA 3 Variables
- Generate OpenVPN Keys
- Configure the OpenVPN Server
- Set Up Firewall and Enable Port Forwarding
- Client Setup
- Testing the Connection
Step 1: Install OpenVPN and Easy-RSA
We will utilize OpenVPN 2.4 and easy-rsa 3 on CentOS 7.6. Ensure you have the ‘epel’ repository installed.
yum install epel-release -y
Proceed to install OpenVPN and Easy-RSA.
yum install openvpn easy-rsa -y
Verify their versions:
openvpn --version ls -lah /usr/share/easy-rsa/
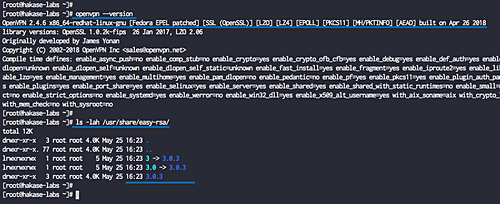
Both OpenVPN 2.4 and easy-rsa 3 are now installed.
Step 2: Configure Easy-RSA 3 Variables
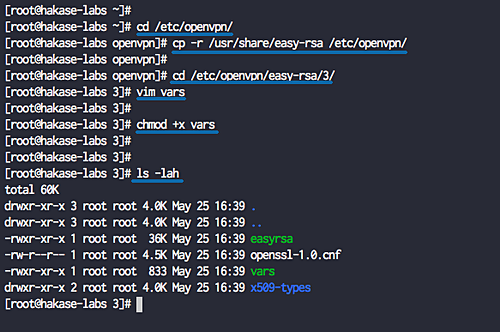
Navigate to the ‘/etc/openvpn/’ directory and copy the easy-rsa script:
cd /etc/openvpn/ cp -r /usr/share/easy-rsa /etc/openvpn/
Create a new ‘vars’ file in the ‘easy-rsa/3/’ directory using vim.
cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3/ vim vars
Add the following configuration settings:
set_var EASYRSA "$PWD" set_var EASYRSA_PKI "$EASYRSA/pki" set_var EASYRSA_DN "cn_only" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_COUNTRY "ID" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_PROVINCE "Jakarta" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_CITY "Jakarta" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_ORG "hakase-labs CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_EMAIL "openvpn@hakase-labs.io" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_OU "HAKASE-LABS EASY CA" set_var EASYRSA_KEY_SIZE 2048 set_var EASYRSA_ALGO rsa set_var EASYRSA_CA_EXPIRE 7500 set_var EASYRSA_CERT_EXPIRE 365 set_var EASYRSA_NS_SUPPORT "no" set_var EASYRSA_NS_COMMENT "HAKASE-LABS CERTIFICATE AUTHORITY" set_var EASYRSA_EXT_DIR "$EASYRSA/x509-types" set_var EASYRSA_SSL_CONF "$EASYRSA/openssl-1.0.cnf" set_var EASYRSA_DIGEST "sha256"
Save and exit. Adjust the configuration variables as needed, such as increasing ‘EASYRSA_KEY_SIZE’ for enhanced security.
chmod +x vars
Step 3: Generate OpenVPN Keys
Using the ‘vars’ file, generate the necessary keys: CA key, server and client keys, DH and CRL PEM files. Start in the easy-rsa directory:
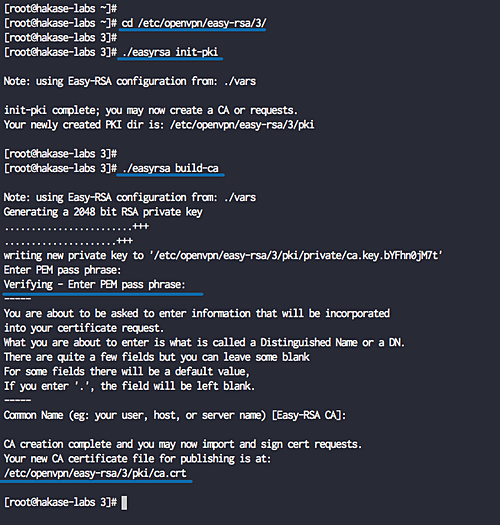
cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/3/
Initialization and Build CA
Initialize the PKI directory and build the CA key:
./easyrsa init-pki ./easyrsa build-ca
Build Server and Client Keys
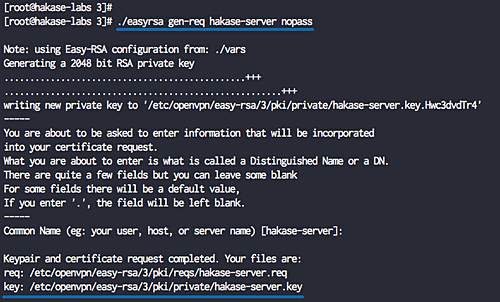
Generate the server and client keys:
./easyrsa gen-req hakase-server nopass ./easyrsa sign-req server hakase-server
./easyrsa gen-req client01 nopass ./easyrsa sign-req client client01
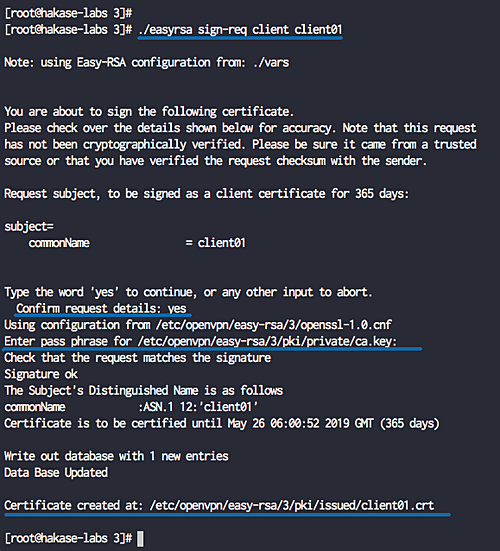
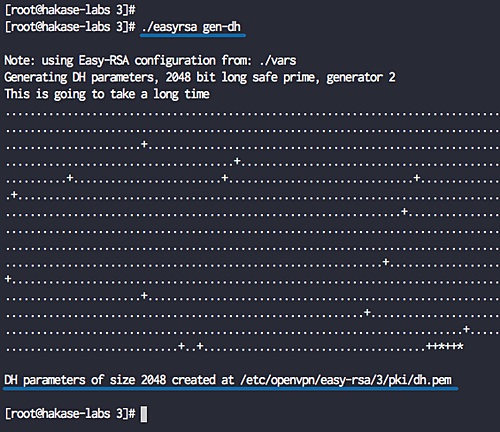
Build Diffie-Hellman and Optional CRL Key
Generate a Diffie-Hellman key:
./easyrsa gen-dh
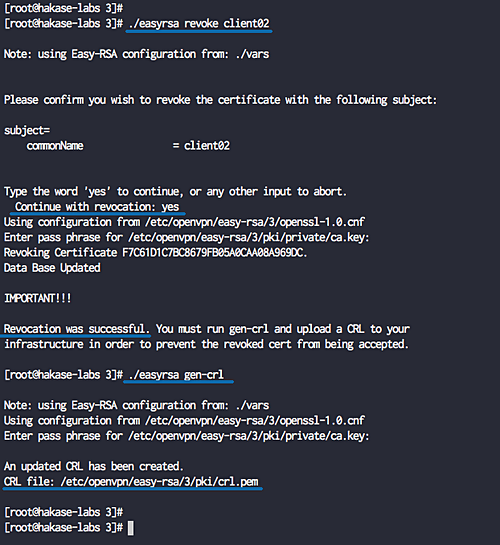
Optionally generate a CRL key for revoking client keys.
./easyrsa revoke someone ./easyrsa gen-crl
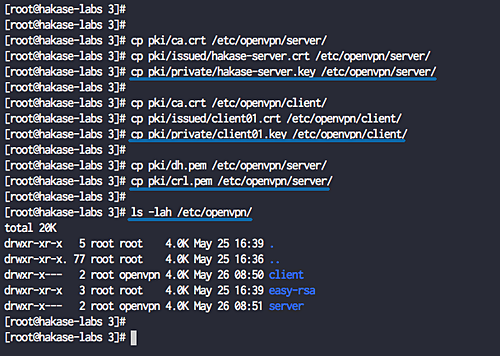
Copy Certificate Files
Copy the generated certificate and key files.
cp pki/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/server/ cp pki/issued/hakase-server.crt /etc/openvpn/server/ cp pki/private/hakase-server.key /etc/openvpn/server/
cp pki/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/client/ cp pki/issued/client01.crt /etc/openvpn/client/ cp pki/private/client01.key /etc/openvpn/client/
cp pki/dh.pem /etc/openvpn/server/ cp pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server/
Step 4: Configure OpenVPN
Create a server configuration file named ‘server.conf’.
cd /etc/openvpn/ vim server.conf
Add the following configuration:
# OpenVPN Port, Protocol and the Tun port 1194 proto udp dev tun # OpenVPN Server Certificate - CA, server key and certificate ca /etc/openvpn/server/ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/server/hakase-server.crt key /etc/openvpn/server/hakase-server.key #DH and CRL key dh /etc/openvpn/server/dh.pem crl-verify /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pem # Network Configuration - Internal network # Redirect all Connection through OpenVPN Server server 10.10.1.0 255.255.255.0 push "redirect-gateway def1" # Using the DNS from https://dns.watch push "dhcp-option DNS 84.200.69.80" push "dhcp-option DNS 84.200.70.40" #Enable multiple client to connect with same Certificate key duplicate-cn # TLS Security cipher AES-256-CBC tls-version-min 1.2 tls-cipher TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-256-GCM-SHA384:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-256-CBC-SHA256:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-128-GCM-SHA256:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-128-CBC-SHA256 auth SHA512 auth-nocache # Other Configuration keepalive 20 60 persist-key persist-tun comp-lzo yes daemon user nobody group nobody # OpenVPN Log log-append /var/log/openvpn.log verb 3
Save and exit the file.
Step 5: Enable Port-Forwarding and Configure Firewall
Activate port forwarding and configure the firewall for OpenVPN:
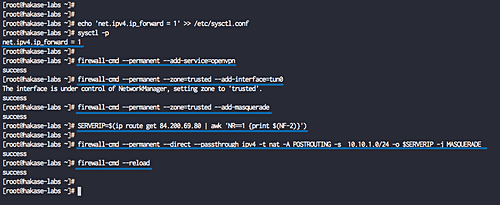
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1' >> /etc/sysctl.conf sysctl -p
Adjust firewall settings:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=openvpn firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-interface=tun0 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=trusted --add-masquerade
Enable NAT:
SERVERIP=$(ip route get 84.200.69.80 | awk 'NR==1 {print $(NF-2)}')
firewall-cmd --permanent --direct --passthrough ipv4 -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.10.1.0/24 -o $SERVERIP -j MASQUERADE
Reload firewall settings and start OpenVPN:
firewall-cmd --reload systemctl start openvpn@server systemctl enable openvpn@server
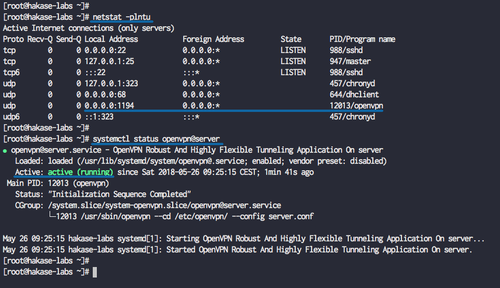
Verify OpenVPN is running:
netstat -plntu systemctl status openvpn@server
Step 6: OpenVPN Client Setup
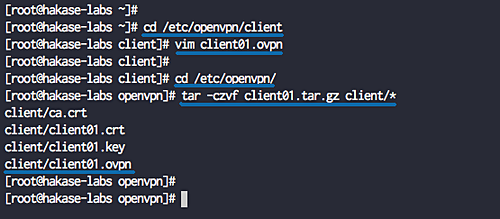
Create a client configuration file ‘client01.ovpn’ in the client directory:
cd /etc/openvpn/client vim client01.ovpn
Add the following client configuration:
client dev tun proto udp remote 139.xx.xx.xx 1194 ca ca.crt cert client01.crt key client01.key cipher AES-256-CBC auth SHA512 auth-nocache tls-version-min 1.2 tls-cipher TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-256-GCM-SHA384:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-256-CBC-SHA256:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-128-GCM-SHA256:TLS-DHE-RSA-WITH-AES-128-CBC-SHA256 resolv-retry infinite compress lzo nobind persist-key persist-tun mute-replay-warnings verb 3
Save and exit. Compress the ‘/etc/openvpn/client’ directory:
cd /etc/openvpn/ tar -czvf client01.tar.gz client/*
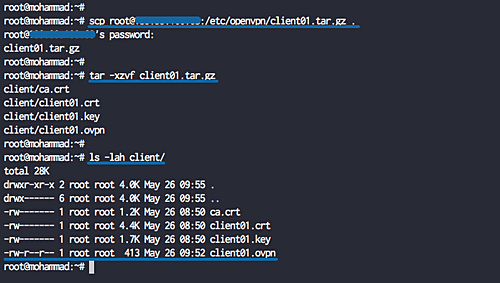
Download the configuration to your local machine using:
scp root@139.xx.xx.xx:/etc/openvpn/client01.tar.gz .
Step 7: Testing OpenVPN
Testing on Linux
Install the necessary packages:
sudo apt install openvpn network-manager-openvpn network-manager-openvpn-gnome -y
To connect, use:
openvpn --config client01.ovpn
Check the connection:
curl ifconfig.io
On Mac OS
Download and install Tunnelblick. After extracting the ‘client01.tar.gz’, rename the directory to ‘client01.tblk’, then double-click to import into Tunnelblick.
On Windows
Download OpenVPN client for Windows and import the configuration.
References
For further reading and resources, visit OpenVPN Documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is OpenVPN?
OpenVPN is an open-source software that allows you to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections over the public Internet.
2. What are the prerequisites for setting up OpenVPN on CentOS?
You will need a CentOS 7.6 server with root access to install OpenVPN.
3. Why do I need a VPN?
VPNs protect your data and identity by encrypting your connection to the internet, making it important for secure browsing, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
4. Can I use OpenVPN on multiple devices?
Yes, you can set up OpenVPN on multiple devices by configuring client keys and configurations for each device.
5. What is Easy-RSA?
Easy-RSA is a CLI utility to build and manage a PKI CA; in this guide, it’s used to generate SSL keys for OpenVPN.
