Automad is a file-based content management system (CMS) and template engine written in PHP. It stores all content in
human-readable text files rather than using a database. This makes an Automad site fully portable, easy to install, and
manageable via version control systems like Git or Mercurial. Despite this simplicity, Automad offers database-like features
such as searching and tagging. Its built-in template engine allows even novice developers and designers to create
aesthetically pleasing themes and templates. This guide will walk you through installing and setting up Automad CMS on a
Debian 10 (buster) system using NGINX as the web server.
Requirements
The following requirements are necessary for installing and running Automad CMS:
- PHP version 5.4 or higher.
- Web server software like Nginx or Apache.
Prerequisites
- A Debian 10 (buster) operating system.
- A non-root user with
sudoprivileges.
Initial Steps
First, verify your Debian version:
lsb_release -ds # Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)
Set the correct timezone:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Update your package lists and upgrade the installed packages to make sure they are up-to-date:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Install essential packages necessary for administering Debian:
sudo apt install -y curl wget vim git unzip socat bash-completion apt-transport-https
Step 1 – Install PHP and Necessary PHP Extensions
Install PHP and the required PHP extensions:
sudo apt install -y php php-cli php-fpm php-common php-mbstring php-xmlrpc php-soap php-gd php-xml php-curl php-zip
To view the installed PHP modules, execute:
php -m # ctype # curl # exif # fileinfo # ...
Confirm the PHP version:
php --version # PHP 7.3.4-2 (cli) (built: Apr 13 2019 19:05:48) ( NTS ) # Copyright (c) 1997-2018 The PHP Group # Zend Engine v3.3.4, Copyright (c) 1998-2018 Zend Technologies # with Zend OPcache v7.3.4-2, Copyright (c) 1999-2018, by Zend Technologies
Note: The PHP-FPM service starts automatically and is enabled on boot in Debian 10.
Step 2 – Install acme.sh Client and Obtain Let’s Encrypt Certificate (optional)
It’s recommended to secure your site with HTTPS. For obtaining a TLS certificate from Let’s Encrypt, you can use the
acme.sh client, a lightweight and zero-dependency shell script.
Install acme.sh:
sudo su - root git clone https://github.com/Neilpang/acme.sh.git cd acme.sh ./acme.sh --install --accountemail your_email@example.com source ~/.bashrc cd ~
Verify the acme.sh version:
acme.sh --version # v2.8.2
Generate RSA and ECC/ECDSA certificates for your domain/hostname:
# RSA 2048 acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength 2048 # ECDSA acme.sh --issue --standalone -d example.com --keylength ec-256
You can add the --staging flag for test certificates.
Certificates and keys will be located at:
- RSA:
/home/username/example.com. - ECC/ECDSA:
/home/username/example.com_ecc.
To list your certificates, execute:
acme.sh --list
Create directories for certificate storage:
mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/example.com sudo mkdir -p /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc
Install and copy certificates to /etc/letsencrypt:
# RSA acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service" # ECC/ECDSA acme.sh --install-cert -d example.com --ecc --cert-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/cert.pem --key-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/private.key --fullchain-file /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.pem --reloadcmd "sudo systemctl reload nginx.service"
Certificates will be auto-renewed every 60 days. Exit from root user and return to a regular sudo user:
exit
Step 3 – Install and Configure NGINX
Install NGINX from the Debian repository:
sudo apt install -y nginx
Verify the NGINX version:
sudo nginx -v # nginx version: nginx/1.14.2
Create an NGINX server block file automad.conf:
server {
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:80;
listen 80;
# RSA
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com/private.key;
# ECC
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/example.com_ecc/private.key;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/automad;
index index.php index.html;
client_max_body_size 100M;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
Link the new configuration file to the NGINX sites-enabled directory:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/automad.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Check for syntax errors in the NGINX configuration:
sudo nginx -t
Reload NGINX:
sudo systemctl reload nginx.service
Step 4 – Install Automad CMS
Create the document root directory for Automad:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/automad
Navigate to the document root:
cd /var/www/automad
Download the latest release of Automad CMS. Remember to update version numbers for newer releases if needed:
sudo curl -O -J -L https://automad.org/download
Uncompress the downloaded archive:
sudo unzip marcantondahmen-automad-6fff2a0456dc.zip
Transfer all Automad files to the document root and remove the downloaded archive:
sudo mv marcantondahmen-automad-6fff2a0456dc/* . && sudo mv marcantondahmen-automad-6fff2a0456dc/.* . sudo rm marcantondahmen-automad-6fff2a0456dc.zip sudo rmdir marcantondahmen-automad-6fff2a0456dc
Set ownership of the /var/www/automad directory to www-data:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/automad
Step 5 – Complete the Automad Installation
To complete the installation, create a user account for using the browser-based Dashboard. Navigate to https://example.com/dashboard and follow the provided instructions.
You will need to create an account before using the Automad dashboard:
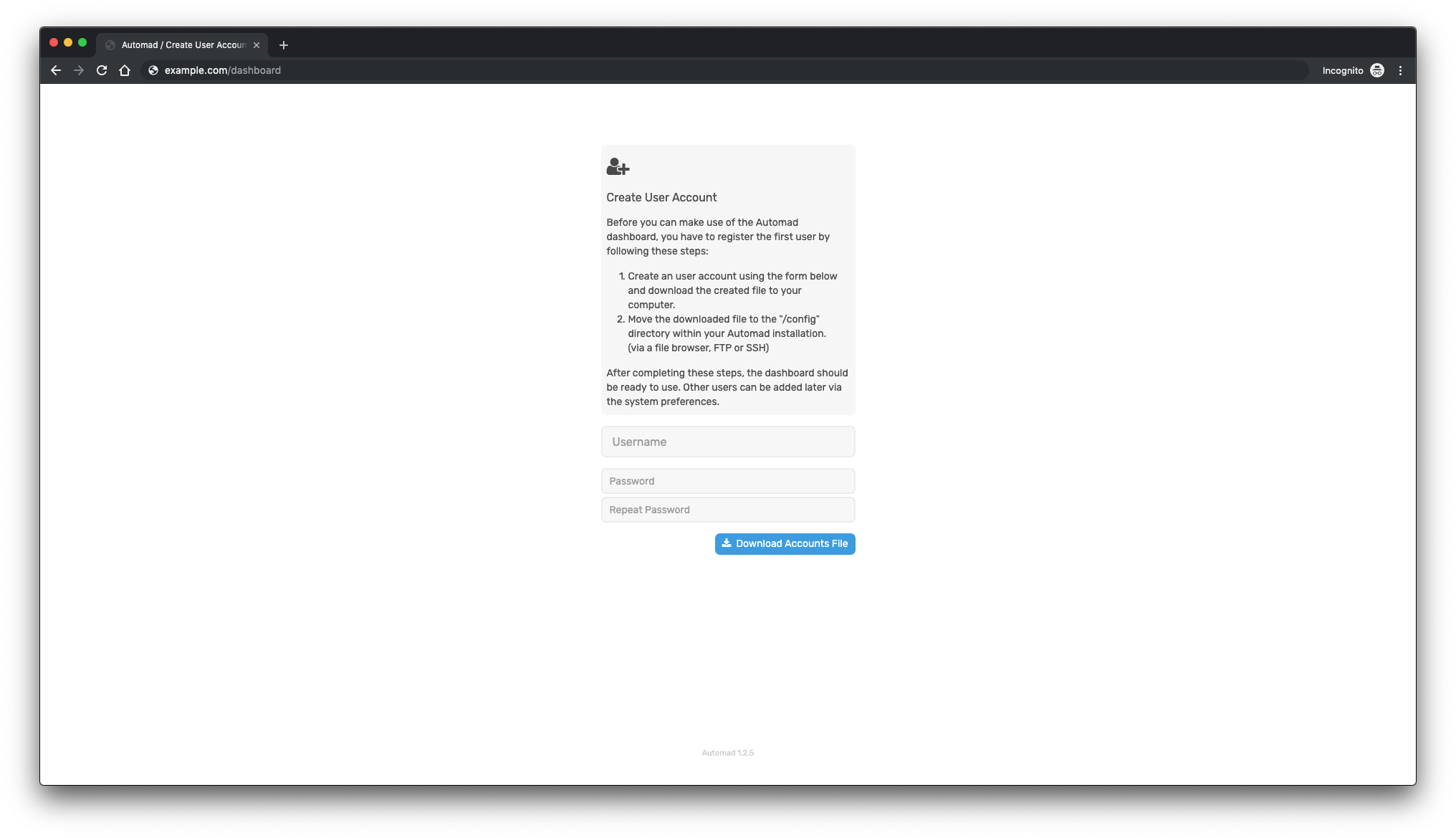
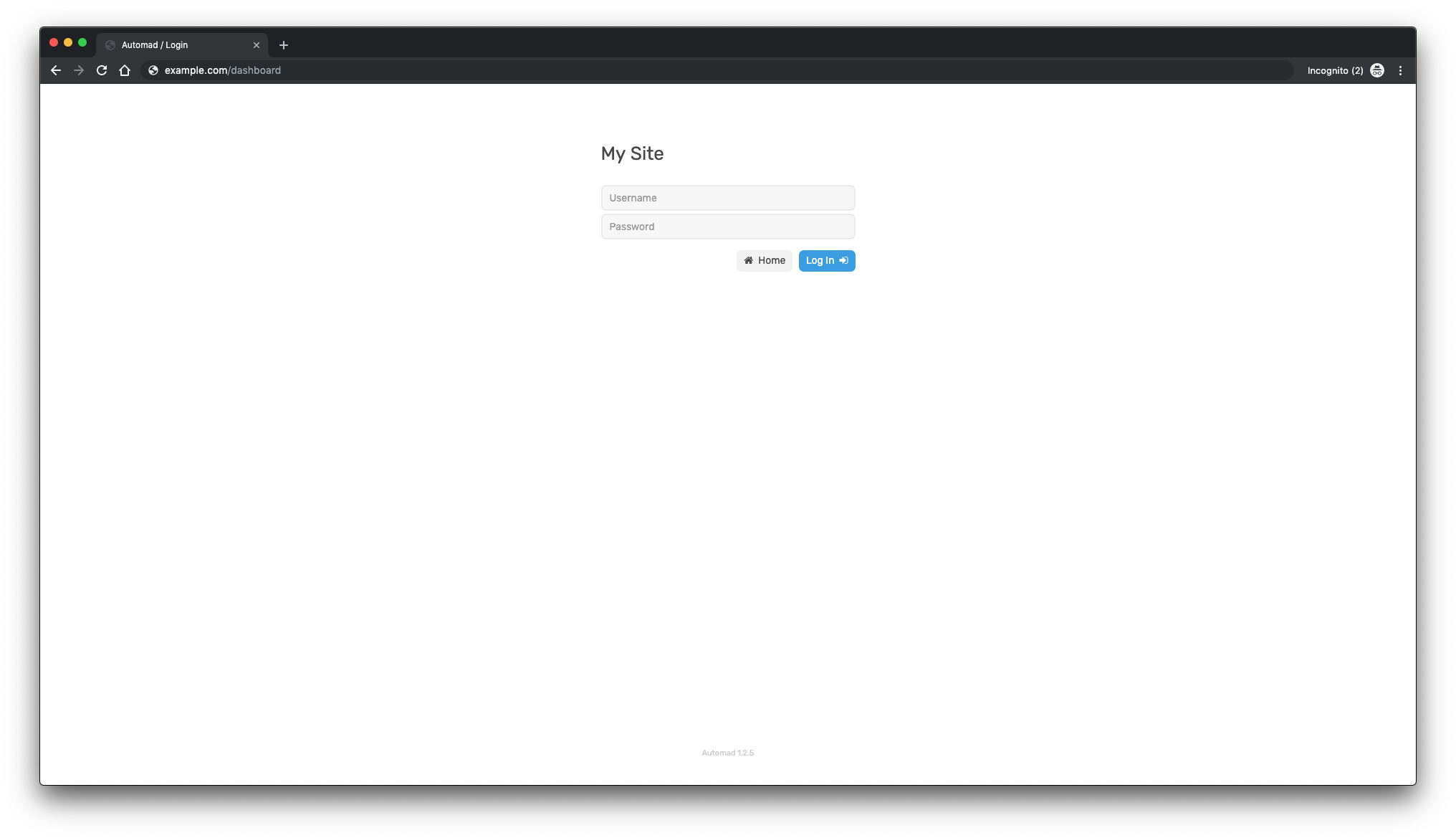
Complete the user account creation and move the generated file to the “/config” directory within the Automad
installation directory. You can then log in to the Automad dashboard:
Once logged in, you’ll see the Automad admin interface:
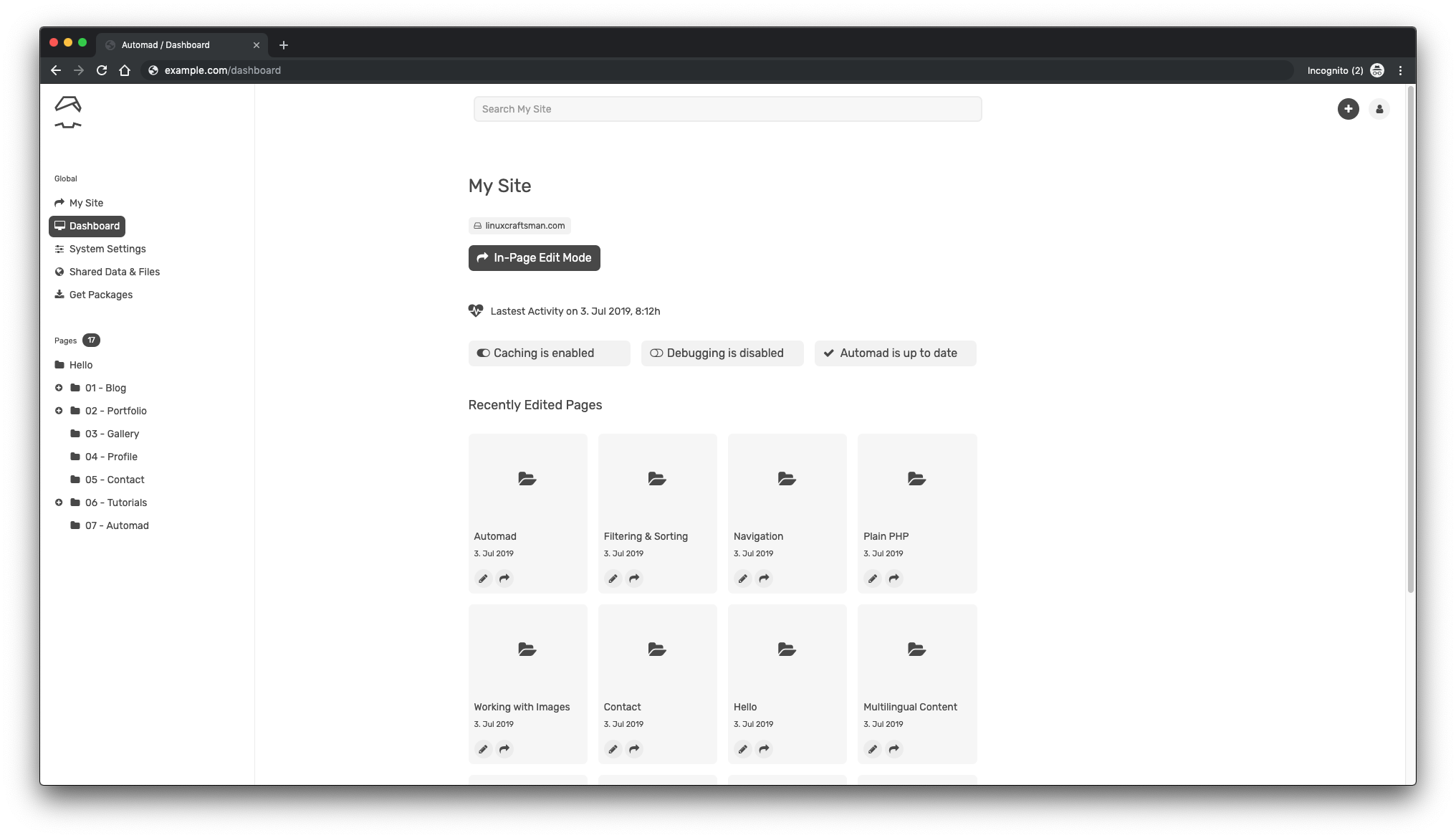
That’s it, you’ve completed the Automad installation.
Links
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Automad?Automad is a file-based CMS and template engine that uses text files to store content instead of a database, making it
easy to install, portable, and version-controlled. - What web servers are compatible with Automad?Automad can work with either Nginx or Apache web servers.
- Why should I secure my site with HTTPS?Securing your site with HTTPS ensures data encryption over the network, making your website more secure.
- Is PHP-FPM required for Automad installation?Yes, PHP-FPM is required to manage PHP processes for serving Automad efficiently.
- How can I ensure my Let’s Encrypt certificates are kept up-to-date?The acme.sh script automatically renews certificates every 60 days, updating them without requiring manual
intervention.