In the previous guide, we covered the installation and setup of Foreman on Ubuntu Server. Now, I will guide you through the process of adding Puppet Agents to Foreman.
Prerequisites
- Foreman Puppet Master
- Root privileges
Objectives
- Set Up Hosts
- Install and Configure Puppet Agent
- Sign Certificates on the Foreman Puppet Master
- Testing
Step 1 – Set Up Hosts
First, configure the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for your puppet agent servers.
Change the server hostname using the command below:
hostnamectl set-hostname client.hakase-labs.io
Edit the ‘/etc/hosts’ file:
vim /etc/hosts
Replace the IP addresses and FQDNs with your own details:
10.9.9.20 server.hakase-labs.io server 10.9.9.21 client.hakase-labs.io client
Save and close the file.
Test the setup to ensure the FQDN is correctly resolved to your valid IP address:
ping $(hostname -f) -c 3
Step 2 – Install and Configure Puppet Agent
This step involves installing Puppet Agent 5 on Ubuntu 18.04 and CentOS 7 servers. Begin by adding the Puppet repository, then install the puppet agent packages on both Ubuntu and CentOS servers.
Install Puppet Agent on Ubuntu 18.04 Server
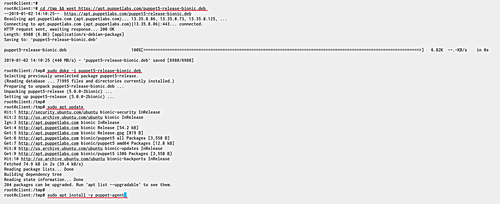
Download and add the repository to your system:
cd /tmp && wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet5-release-bionic.deb sudo dpkg -i puppet5-release-bionic.deb
Update Ubuntu repositories and install puppet agent packages:
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y puppet-agent
Install Puppet Agent on CentOS 7 Server
Download and add the repository to your system:
cd /tmp && wget https://yum.puppet.com/puppet5/puppet5-release-el-7.noarch.rpm rpm -ivh puppet5-release-el-7.noarch.rpm
Install puppet agent packages:
sudo yum install -y puppet-agent
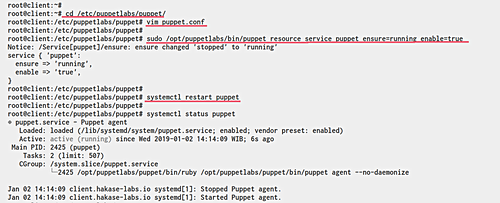
Editing the default puppet configuration is necessary. Define the agent settings by editing ‘puppet.conf’:
cd /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ vim puppet.conf
Replace with your server FQDN and certname:
[agent] server = server.hakase-labs.io certname = client.hakase-labs.io runinterval = 180 environment = production listen = false pluginsync = true report = true
Save and exit. Start the puppet agent service:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet resource service puppet ensure=running enable=true
If needed, restart the service:
sudo systemctl restart puppet
Puppet agent is now active on both Ubuntu and CentOS servers.
Step 3 – Sign Certificate Requests of the Puppet Agents
You can sign certificate requests directly from the puppet master server terminal or via the Foreman dashboard.
Sign Certificate Requests using Terminal Shell
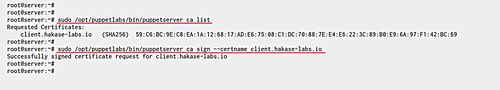
Log in to the puppet master server and check the certificate request:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca list
Sign the client certificate:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppetserver ca sign --certname client.hakase-labs.io
The puppet agent certificate is now added to the puppet master.
Sign Certificate Requests using the Foreman Dashboard
Click on the ‘Infrastructure‘ menu, then ‘Smart Proxies‘.
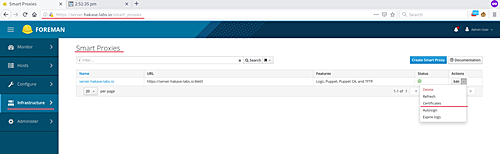
Select ‘Certificates‘ from the dropdown:
You will see the client’s pending request; simply click ‘Sign‘.
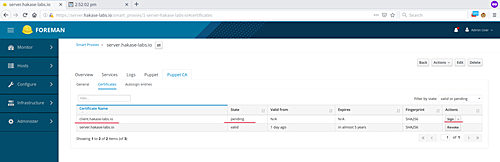
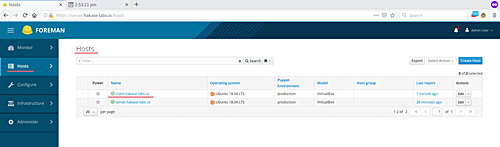
Verify agent hosts by navigating to the ‘Hosts’ page and ensuring your puppet agent appears in the list:
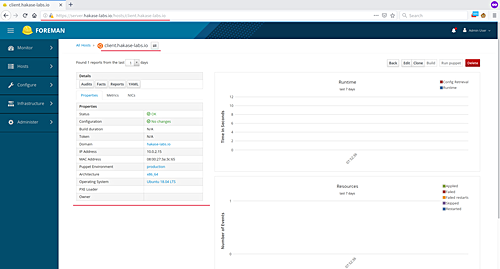
Details about the Ubuntu Puppet Agent:
Step 4 – Testing
Test the puppet foreman server and puppet agent by deploying the nginx and NTP services to the puppet agent host. Initially, download the modules for these services to the foreman server, activate them, and add to the puppet agent.
Download Nginx Puppet Module
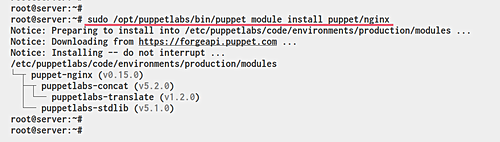
Run the following command on the puppet master server:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet module install puppet/nginx
Activate Puppet Modules
Import the nginx module via the foreman dashboard:
Click the ‘Configure‘ menu then ‘Puppet Classes‘.
Select ‘Import Environment from server.hakase-labs.io‘, tick the available module classes, and click ‘Update‘.
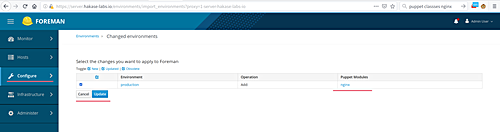
The nginx module will now appear in the list:
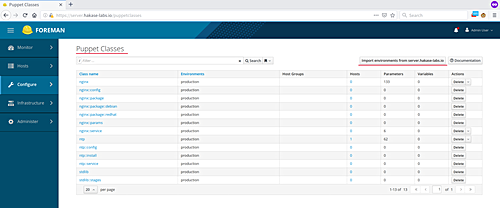
Add Puppet Module to Agent Host
Navigate to ‘Hosts‘ and click ‘All Hosts‘ to see available hosts:
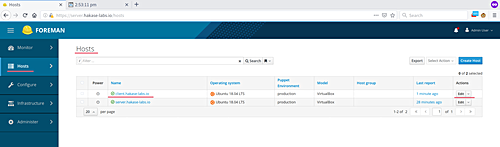
Select the ‘Edit‘ button for ‘client.hakase-labs.io’.
Under ‘Puppet Classes‘, add the ‘nginx’ and ‘ntp’ modules, then click ‘Submit‘.
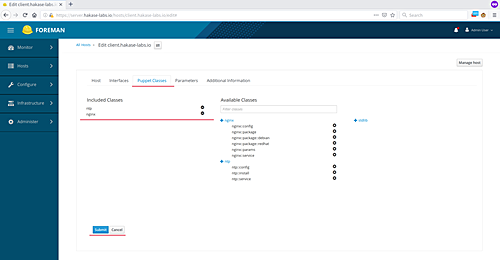
The Nginx and NTP modules are now added to the Agent host.
Additional: Verify active classes by clicking ‘YAML‘ on host details, displaying the raw YAML configuration.

Apply and Test
Apply changes manually with the following command on puppet agent hosts:
sudo /opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
The result will display as follows:
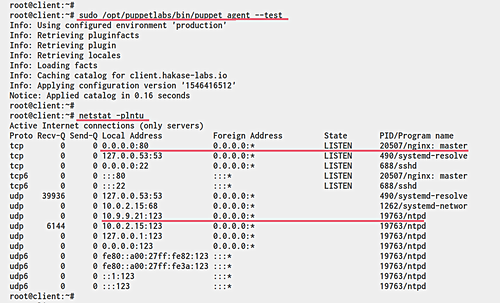
Verify nginx and ntp services by checking ports:
netstat -plntu
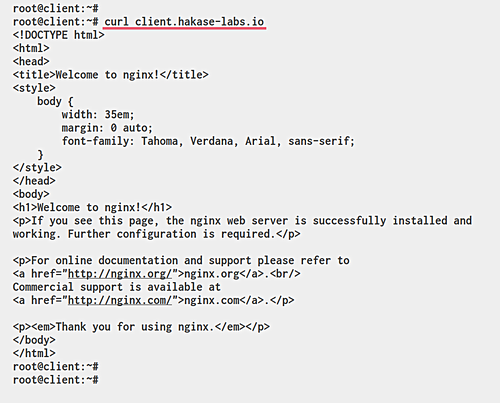
Access the nginx web server on the agent node:
curl client.hakase-labs.io
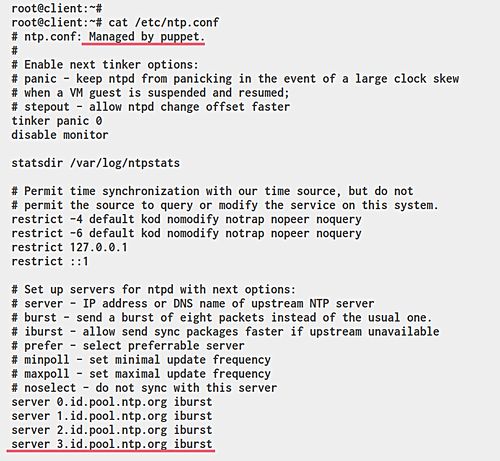
Verify the ntp configuration:
cat /etc/ntp.conf
The configuration will show NTP management by Puppet:
Links
FAQ
What is Foreman?
Foreman is a complete lifecycle management tool for physical and virtual servers. It allows administrators to provision, configure, and manage servers.
Why should I use Puppet with Foreman?
Puppet enables automation in configuration management, which complements Foreman’s ability to provision and monitor system states.
Can I use other operating systems besides Ubuntu and CentOS?
Yes, Puppet and Foreman support a range of operating systems. Check the official documentation for compatibility details.
What should I do if my certificate request fails?
If a certificate request fails, ensure the puppet agent and master are correctly configured with matching FQDNs and network settings. Check logs for more information.
How frequently does Puppet check for updates by default?
Puppet checks for updates every 30 minutes by default, as set by the runinterval.
