Cockpit is a versatile and open-source server management dashboard that simplifies Linux server administration through a web browser. It serves as a web-based control panel, particularly beneficial for users less acquainted with the Linux command line. With Cockpit, you can oversee CPU usage, analyze filesystem metrics, manage processes, and much more. Furthermore, it facilitates various system administration tasks, including user management, network troubleshooting, and file transfers.
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to installing and utilizing Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04.
- A configured root password on your server.
Install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04
Cockpit is readily available in the default Ubuntu 22.04 repository. Install it with the following command:
apt-get install cockpit -y
To enhance functionality, install the Podman module with:
apt-get install cockpit-podman -y
After installation, activate the Cockpit service and configure it to initiate during system reboot:
systemctl start cockpit systemctl enable cockpit
To verify the Cockpit service status, use:
systemctl status cockpit
The expected output should resemble:
? cockpit.service - Cockpit Web Service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.service; static)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-12-05 15:15:24 UTC; 8s ago
TriggeredBy: ? cockpit.socket
Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8)
Process: 16161 ExecStartPre=/usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-certificate-ensure --for-cockpit-tls (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 16176 (cockpit-tls)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4579)
Memory: 956.0K
CPU: 363ms
CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.service
??16176 /usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-tls
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Starting Cockpit Web Service...
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 cockpit-certificate-ensure[16168]: /usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-certificate-helper: line 32: sscg: command not found
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 cockpit-certificate-ensure[16169]: ..+...+..+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++*....>
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 cockpit-certificate-ensure[16169]: ...+...........+...+..........+..+...+.+.....+.......+..+.+..+....+.........+..>
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 cockpit-certificate-ensure[16169]: -----
Dec 05 15:15:24 ubuntu2204 systemd[1]: Started Cockpit Web Service.
At this stage, Cockpit is operational and set to listen on port 9090. Confirm this by executing:
ss -antpl | grep 9090
Your results should display:
LISTEN 0 4096 *:9090 *:* users:(("cockpit-tls",pid=16176,fd=3),("systemd",pid=1,fd=61))
Configure UFW Firewall
If your system has UFW firewall set up, you must permit access through ports 80 and 9090.
Allow these ports by executing:
ufw allow 9090 ufw allow 80
Reload the UFW rules with:
ufw reload
Examine the UFW firewall rules status with:
ufw status
The output should include:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22 ALLOW Anywhere 80 ALLOW Anywhere 9090 ALLOW Anywhere 22 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 9090 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Access Cockpit Web Interface
To access the Cockpit web interface, open a browser and navigate to https://your-server-ip:9090. You should encounter the following Cockpit login page:
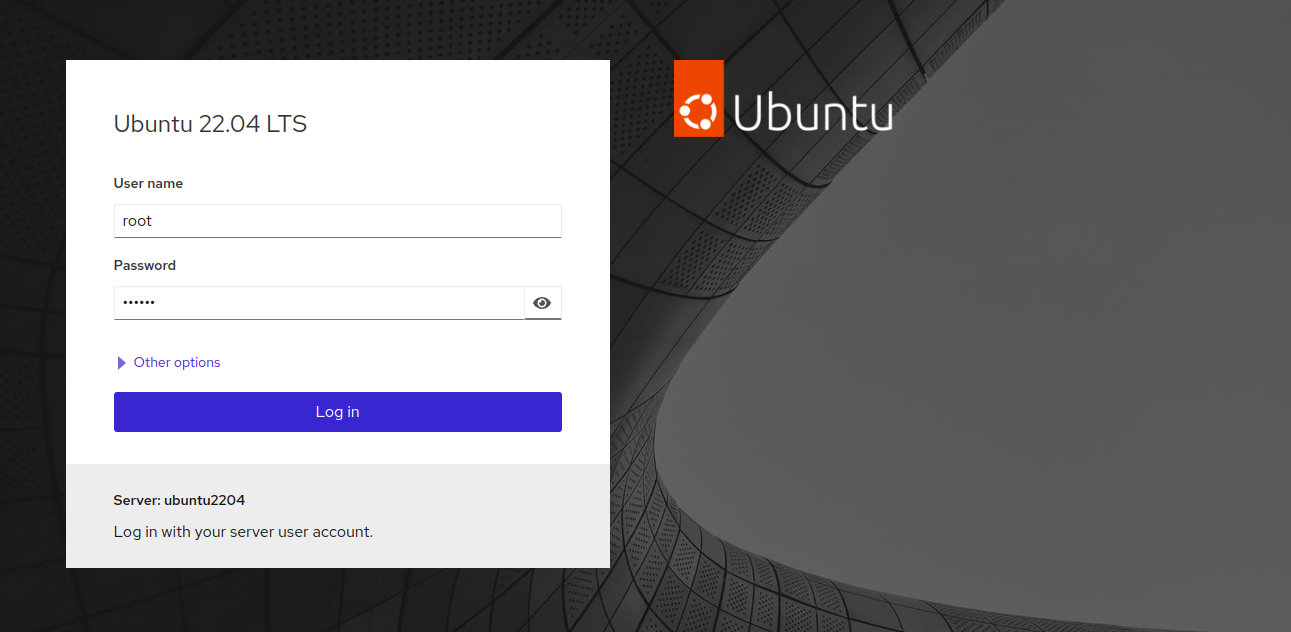
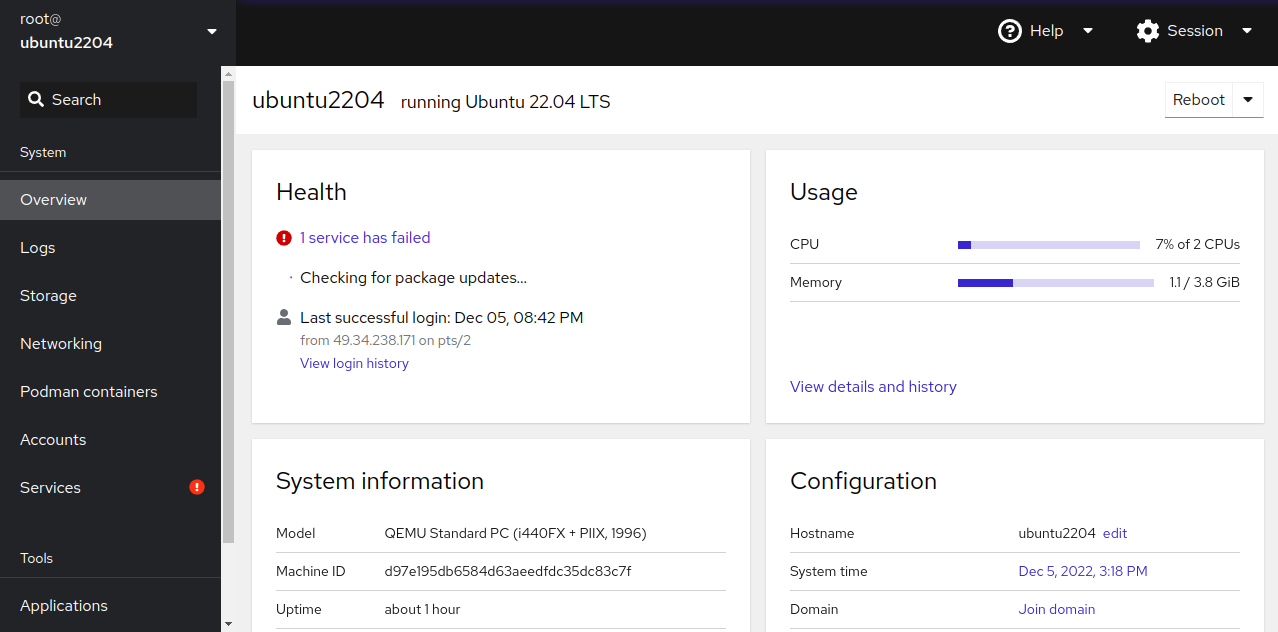
Enter the root username and password, then click Login. The Cockpit dashboard will then appear:
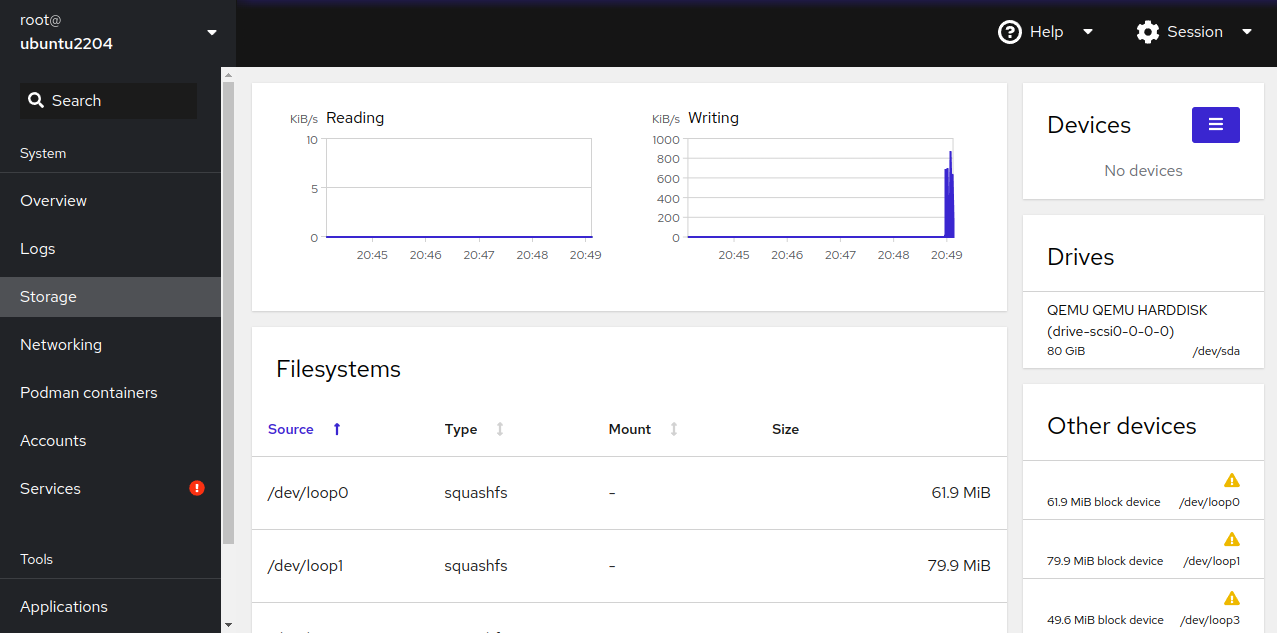
By selecting options like Storage from the left pane, you can view partition details:
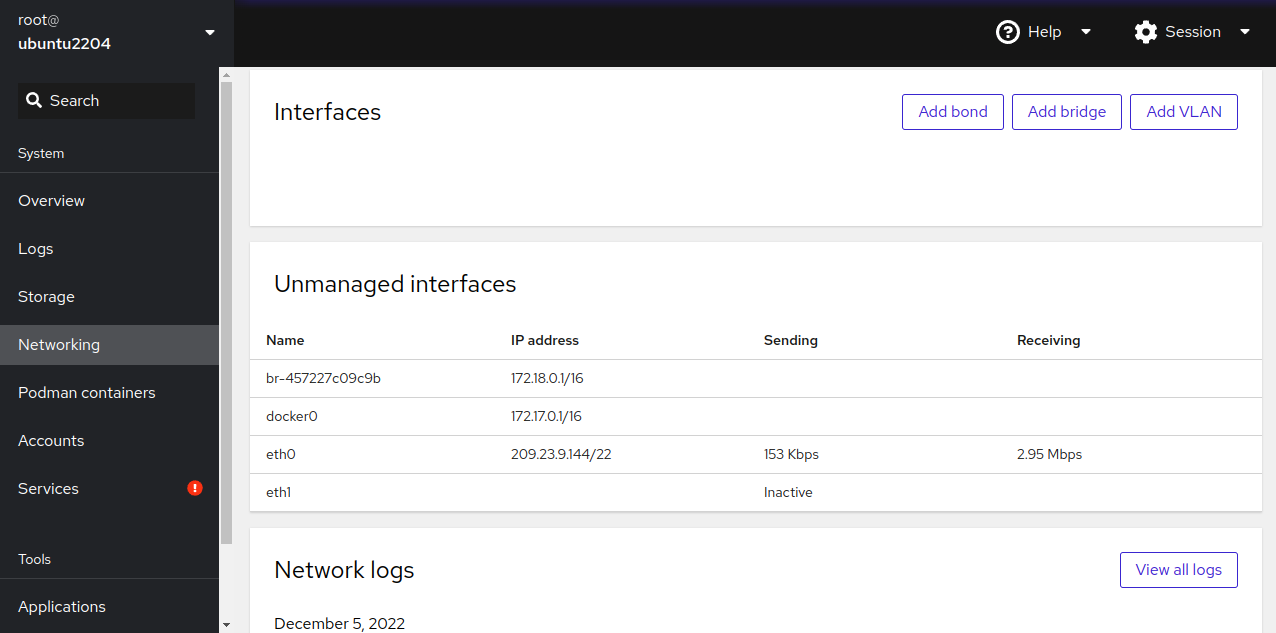
Click on Networking to see network information:
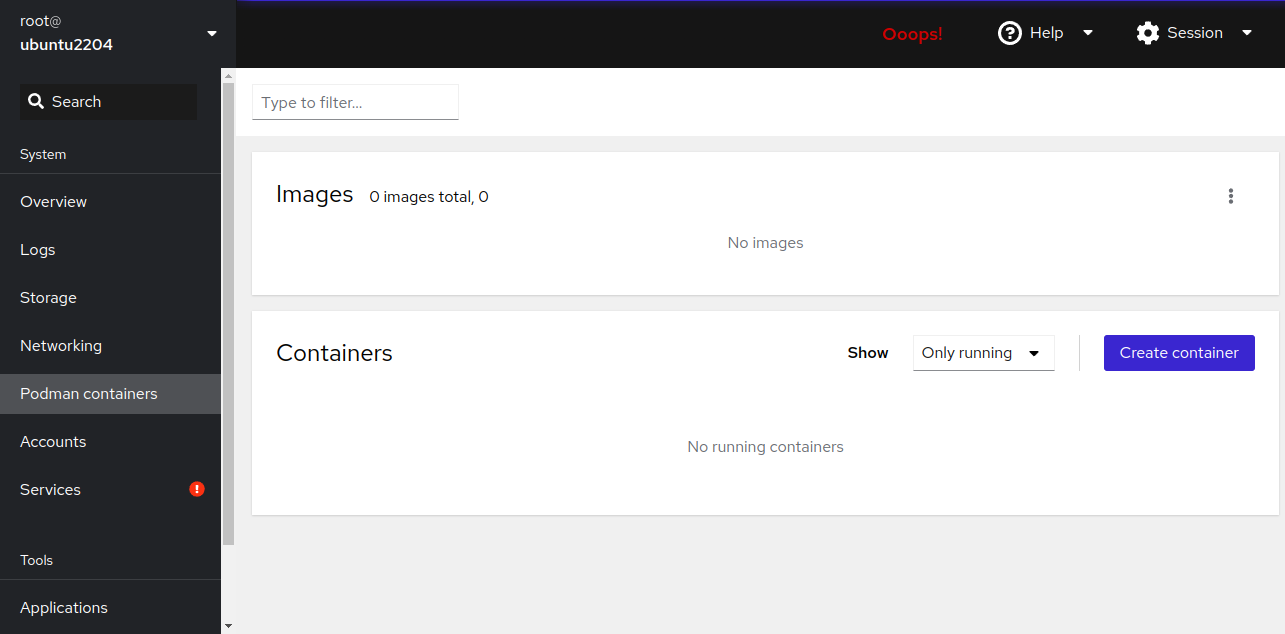
Under Podman Containers, find details about containers and images:
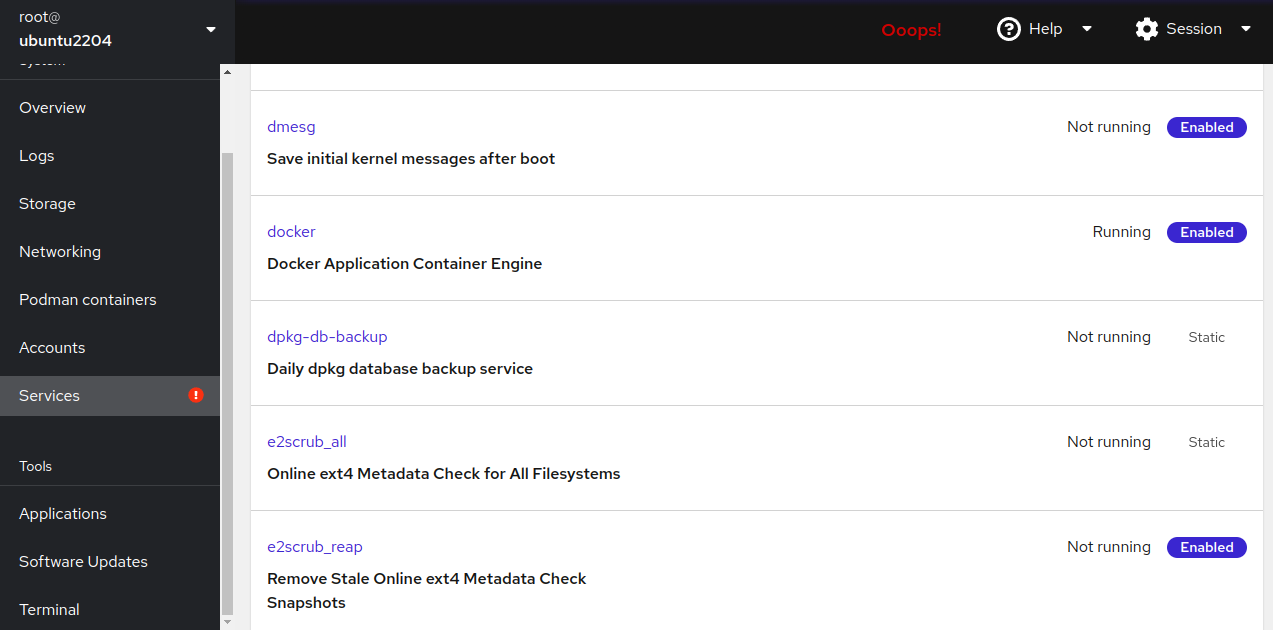
The Services section displays all available system services.
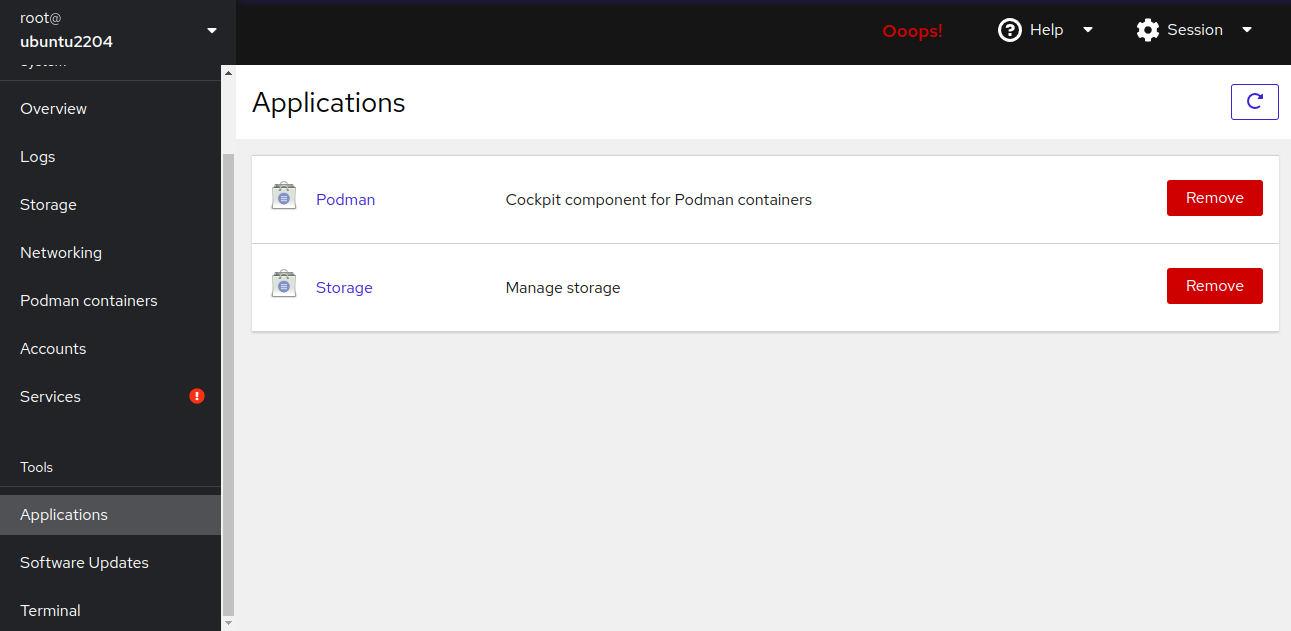
Explore Applications for a list of all installed applications:
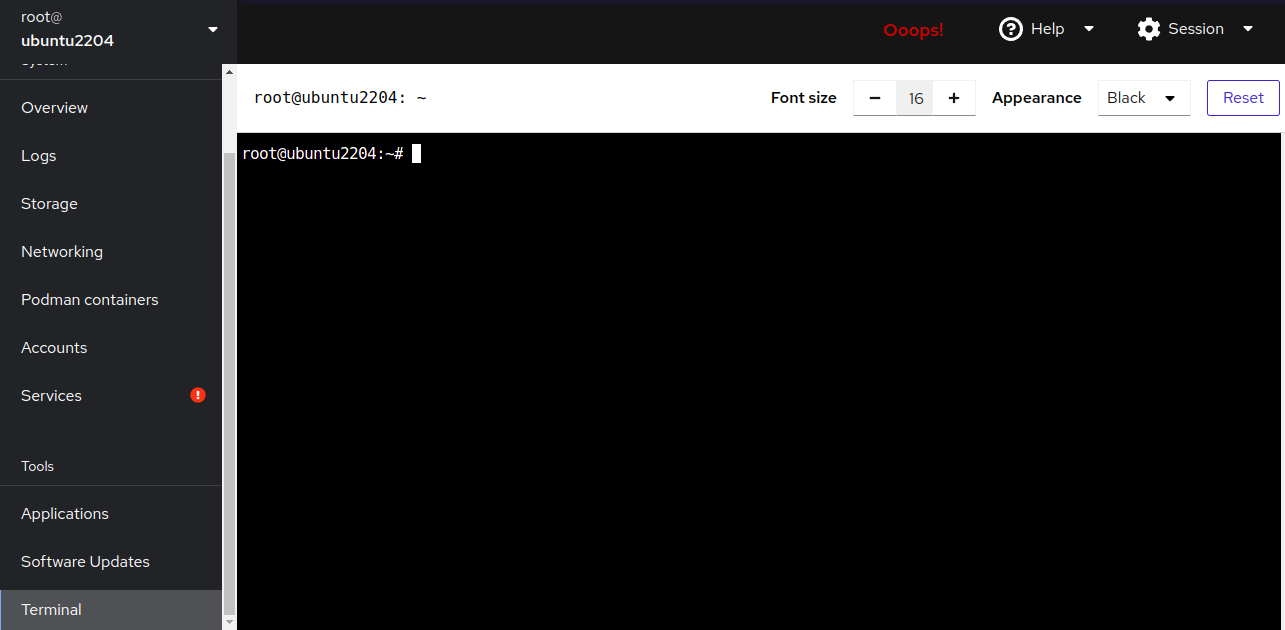
The Terminal option lets you directly interact with the server’s command line.
Frequently Asked Questions about Cockpit Web Console
What is Cockpit Web Console?
The Cockpit Web Console is a user-friendly, web-based interface for server management. It enables administrators to perform tasks like system monitoring, service management, storage configuration, and network setting management on Ubuntu servers.
How do I access the Cockpit Web Console?
Post-installation, access the Cockpit Web Console by entering https://<your-server-ip>:9090 in a web browser, replacing <your-server-ip> with your server’s IP address.
Do I need special permissions to use Cockpit?
Administrative privileges are required on the Ubuntu server to perform most tasks within Cockpit. Typically, you log in using your system user account and password.
Is Cockpit secure?
Yes, Cockpit is built with security in mind, using HTTPS for encryption and requiring user authentication. It integrates seamlessly with Ubuntu firewalls and SELinux policies.
Can I manage multiple servers with Cockpit?
Absolutely. Cockpit allows centralized management of various servers through a single interface. You can add and connect multiple servers in the Cockpit dashboard.
What kind of system information can I view in Cockpit?
Cockpit provides extensive insights into system performance, including CPU, memory, disk usage, network activity, and more. It also includes logs, service status, and system update capabilities.
Can I use Cockpit to manage Docker containers?
Yes, Cockpit supports Docker container management. Install the Cockpit Docker module to access this feature.
Is it possible to configure network settings through Cockpit?
Indeed, Cockpit facilitates network configuration, allowing adjustments to IP addresses, routing, and DNS settings via its web interface.
How do I update Cockpit?
Updating Cockpit is straightforward. Run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
This will ensure you have the most recent version of Cockpit.
Is there any cost associated with using Cockpit?
No, Cockpit is a free and open-source tool.
Where can I find more documentation on Cockpit?
For more comprehensive documentation and guides, visit the official Cockpit website or the Ubuntu documentation pages.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04. Cockpit is a powerful tool for managing and configuring Linux-based servers. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out.
