Gitea is a free, open-source, self-hosted Git server written in the Go programming language, offering a robust and scalable version control platform similar to GitHub. It includes numerous features such as issue and time tracking, repository branching, file locking, tagging, merging, and more. If you’re in search of a self-hosted Git service, Gitea is an excellent choice.
This tutorial will guide you through the process of installing Gitea on Debian 11.
Prerequisites
- A server running Debian 11.
- A root password configured on the server.
Install and Configure MariaDB Database
To use Gitea, you must have MariaDB/MySQL installed as a database backend. If it’s not installed yet, run the following command:
apt-get install mariadb-server -y
After installation, secure the MariaDB instance by setting a password and completing the security script:
mysql_secure_installation
Follow the prompts and answer as shown below:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): OK, successfully used password, moving on... Set root password? [Y/n] Y Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Next, connect to the MariaDB interface:
mysql -u root -p
Create a database and user for Gitea:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE gitea; MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON gitea.* TO 'gitea'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Flush privileges and exit:
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; MariaDB [(none)]> QUIT;
Install Gitea
Create a dedicated Gitea user:
adduser --system --shell /bin/bash --gecos 'Git Version Control' --group --disabled-password --home /opt/git git
Example output:
Adding system user `git' (UID 109) ... Adding new group `git' (GID 115) ... Adding new user `git' (UID 109) with group `git' ... Creating home directory `/opt/git' ...
Download the latest version of Gitea:
curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/go-gitea/gitea/releases/latest |grep browser_download_url | cut -d '"' -f 4 | grep '\linux-amd64$' | wget -i -
Move the Gitea binary to your system path:
mv gitea-*-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/gitea
Make the Gitea binary executable:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitea
Verify the Gitea version:
gitea --version
Example output:
Gitea version 1.15.3 built with GNU Make 4.1, go1.16.8 : bindata, sqlite, sqlite_unlock_notify
Create the directory structure for Gitea:
mkdir -p /etc/gitea /var/lib/gitea/{custom,data,indexers,public,log}
Set permissions and ownership:
chown git:git /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chmod 750 /var/lib/gitea/{data,indexers,log}
chown root:git /etc/gitea
chmod 770 /etc/gitea
Create a Systemd Service File for Gitea
Create a systemd service file for Gitea:
nano /etc/systemd/system/gitea.service
Add the following content:
[Unit] Description=Gitea (Git with a cup of tea) After=syslog.target After=network.target After=mysql.service [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity LimitNOFILE=65535 RestartSec=2s Type=simple User=git Group=git WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/gitea/ ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini Restart=always Environment=USER=git HOME=/opt/git GITEA_WORK_DIR=/var/lib/gitea [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save the file, reload the systemd daemon, then start and enable Gitea:
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start gitea systemctl enable gitea
Check the Gitea service status:
systemctl status gitea
Example output:
? gitea.service - Gitea (Git with a cup of tea)
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gitea.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-10-02 12:59:27 UTC; 9s ago
Main PID: 19179 (gitea)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 4679)
Memory: 128.3M
CPU: 1.415s
CGroup: /system.slice/gitea.service
??19179 /usr/local/bin/gitea web -c /etc/gitea/app.ini
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 cmd/web.go:102:runWeb() [I] Starting Gitea on PID: 19179
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/setting/setting.go:569:NewContext() [W] Custom config '/etc/gitea/app.ini' not>
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:21:PreloadSettings() [I] AppPath: /usr/local/bin/gitea
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:22:PreloadSettings() [I] AppWorkPath: /var/lib/gitea
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:23:PreloadSettings() [I] Custom path: /var/lib/gitea/custom
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:24:PreloadSettings() [I] Log path: /var/lib/gitea/log
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:25:PreloadSettings() [I] Preparing to run install page
Oct 02 12:59:28 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:28 ...s/install/setting.go:28:PreloadSettings() [I] SQLite3 Supported
Oct 02 12:59:29 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:29 cmd/web.go:196:listen() [I] Listen: http://0.0.0.0:3000
Oct 02 12:59:29 debian11 gitea[19179]: 2021/10/02 12:59:29 ...s/graceful/server.go:62:NewServer() [I] Starting new Web server: tcp:0.0.0.0:300>
Gitea is now running on port 3000. Verify the service is listening on this port:
ss -antpl | grep 3000
Example output:
LISTEN 0 4096 *:3000 *:* users:(("gitea",pid=19179,fd=6))
Configure Nginx for Gitea
Install and configure Nginx as a reverse proxy:
apt-get install nginx -y
Create an Nginx virtual host file:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/gitea.conf
Add the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name gitea.example.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/gitea_access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/gitea_error.log;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
}
}
Verify Nginx configuration and restart the service:
nginx -t systemctl restart nginx
Check Nginx status:
systemctl status nginx
Example output:
? nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-10-02 13:00:33 UTC; 4s ago
Docs: man:nginx(8)
Process: 19209 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 19211 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 19212 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 4679)
Memory: 3.2M
CPU: 50ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??19212 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;
??19213 nginx: worker process
??19214 nginx: worker process
Oct 02 13:00:33 debian11 systemd[1]: Starting A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server...
Oct 02 13:00:33 debian11 systemd[1]: Started A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server.
Edit the Gitea app.ini to set domain info:
nano /etc/gitea/app.ini
Modify these lines:
DOMAIN = gitea.example.com ROOT_URL = http://gitea.example.com/
Save changes and restart Gitea:
systemctl restart gitea
Access Gitea Web Interface
Open a browser and navigate to http://gitea.example.com. You should see the Gitea setup page:
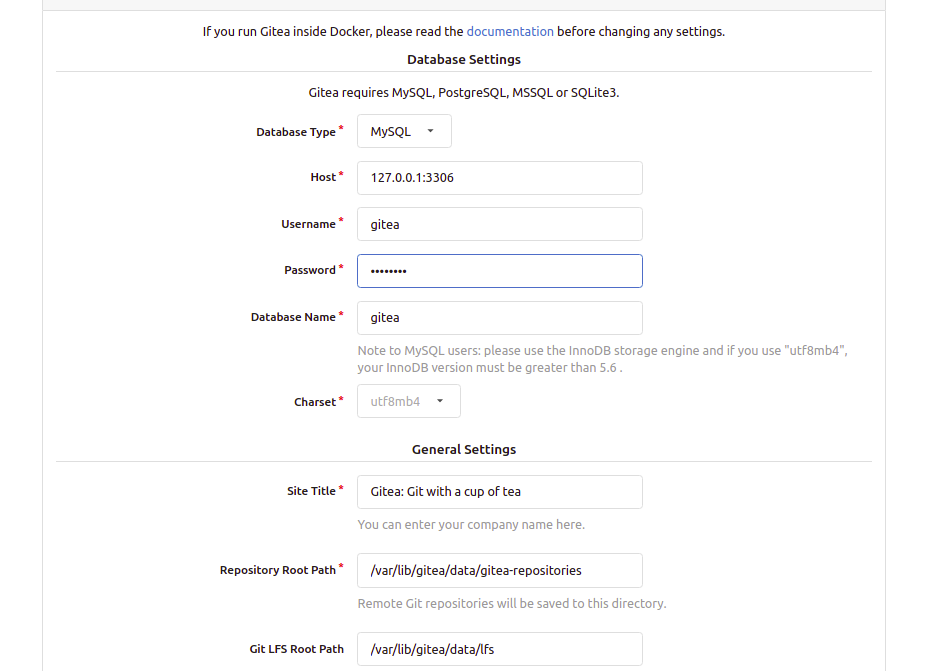
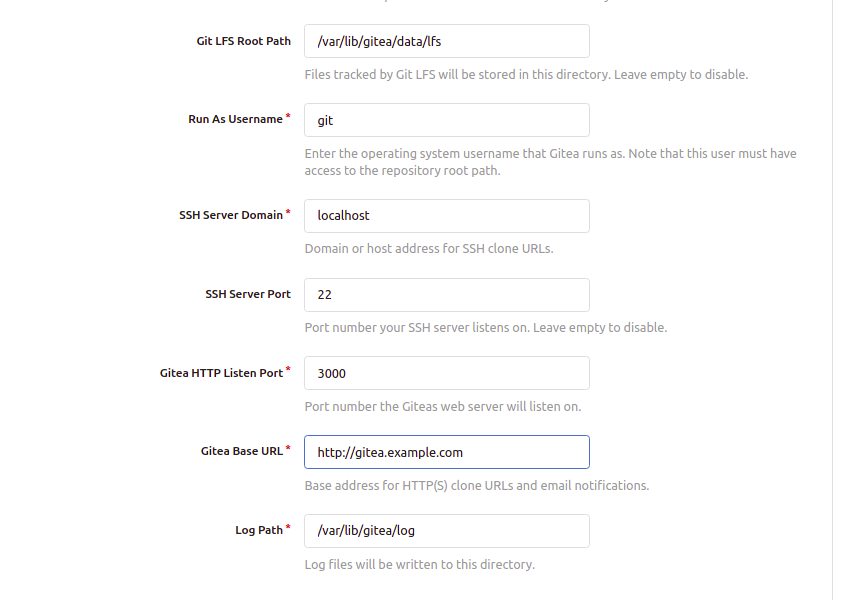
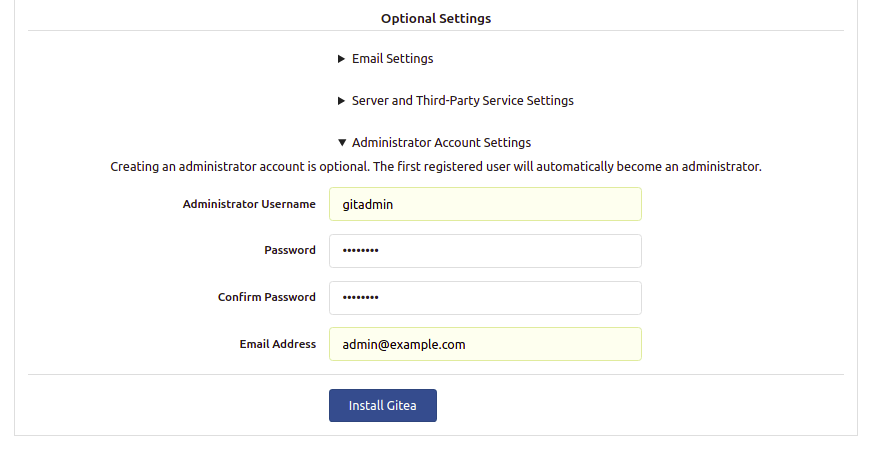
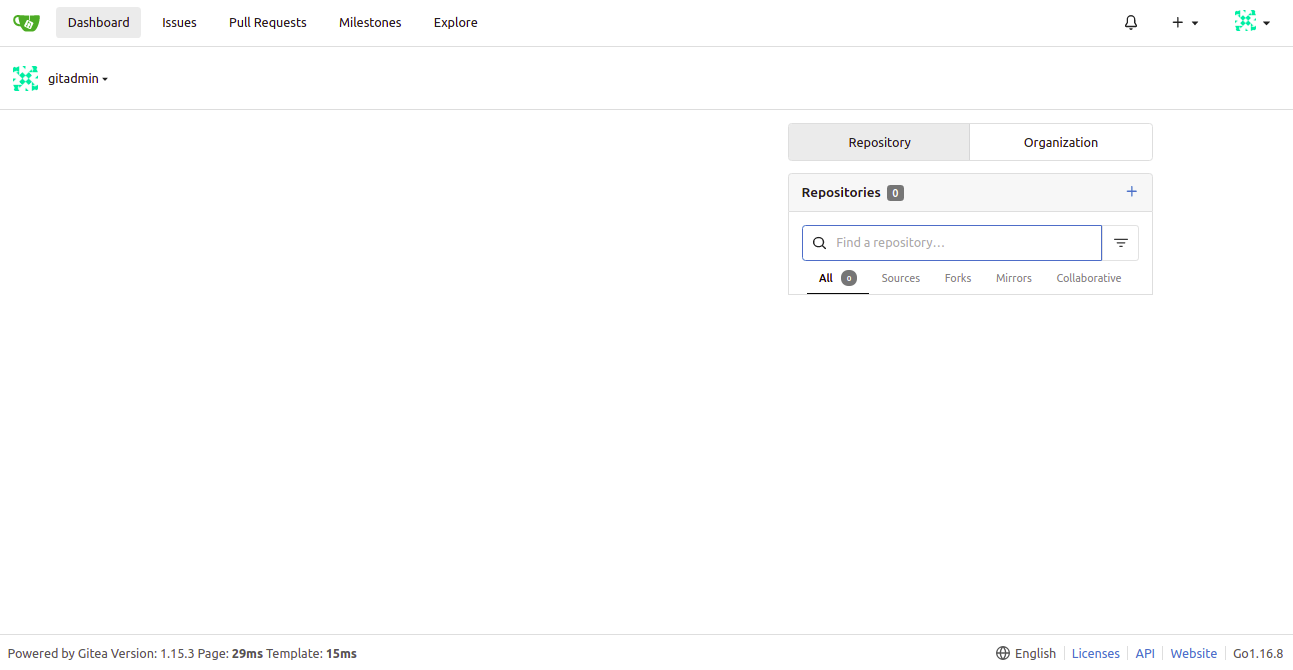
Provide your Gitea database information, URL, admin username, password, port, and click on Install Gitea. You should see the Gitea dashboard:
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully set up Gitea with Nginx proxy on Debian 11. This setup will enhance project management in your development environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Gitea used for?
Gitea is used for managing Git repositories with a focus on providing a self-hosted environment similar to GitHub, equipped with essential features for software development collaboration.
Why use a reverse proxy with Nginx?
Using Nginx as a reverse proxy helps in directing client requests to Gitea efficiently, enhancing security and managing different web apps running on the same server.
Can I use a different database instead of MariaDB?
Yes, Gitea supports multiple databases, including PostgreSQL and SQLite, though MariaDB/MySQL is commonly used.
What are the benefits of using Gitea over GitHub?
Gitea offers the flexibility of self-hosting, allowing customization and complete control over your code hosting, unlike the proprietary offerings of GitHub.
