Graylog is a robust, free, and open-source log monitoring tool that empowers users to capture, store, and analyze vast quantities of machine data in real-time. It’s specifically designed for modern log analytics, enabling users to swiftly derive meaningful insights from data and take timely action. With built-in alert systems and historical log searches, Graylog utilizes ElasticSearch as its primary index database and MongoDB for metadata storage. It effectively facilitates the monitoring, searching, and analysis of extensive data volumes in a user-friendly format.
This guide will demonstrate how to install Graylog on an Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04 with at least 4GB of RAM.
- A root password configured on the server.
Getting Started
To begin, update your system packages to their latest versions using the following commands:
apt update -y apt upgrade
Once the packages are updated, you must install several dependencies on your server. Run the following command to install them:
apt install apt-transport-https gnupg2 uuid-runtime pwgen curl dirmngr -y
After installing the necessary dependencies, proceed to the next step.
Install Java JDK
Graylog requires Java, which you can install with the following command:
apt install openjdk-11-jre-headless -y
Verify the installed Java version by running:
java -version
The output should resemble:
openjdk version "11.0.16" 2022-07-19 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 11.0.16+8-post-Ubuntu-0ubuntu122.04) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 11.0.16+8-post-Ubuntu-0ubuntu122.04, mixed mode, sharing)
Install and Configure Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is crucial for Graylog as it stores logs from external sources. Follow these steps to install it:
Add the Elasticsearch repository by downloading and adding its GPG key:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | apt-key add -
Add the repository:
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
Finally, install Elasticsearch:
apt update -y apt install elasticsearch-oss -y
Edit the Elasticsearch configuration file to define the cluster name:
nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Add the following lines:
cluster.name: graylog action.auto_create_index: false
Start and enable Elasticsearch to automatically start at boot:
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start elasticsearch systemctl enable elasticsearch
Verify Elasticsearch status:
systemctl status elasticsearch
Test Elasticsearch response:
curl -X GET http://localhost:9200
You should see a JSON response denoting a successful installation.
Install MongoDB Server
Graylog utilizes MongoDB as a database. To install it, add the MongoDB repository:
wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.4.asc | apt-key add - echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/4.4 multiverse" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.4.list
Execute the following commands to install MongoDB:
apt update -y apt install -y mongodb-org
Start and enable MongoDB:
systemctl enable --now mongod
Verify MongoDB status:
systemctl status mongod
Install and Configure Graylog
To install Graylog, first download its repository package:
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-4.3-repository_latest.deb
Install the package:
dpkg -i graylog-4.3-repository_latest.deb
Update package lists and install the Graylog server:
apt update -y apt install graylog-server -y
Generate a secret to secure user passwords:
pwgen -N 1 -s 96
Create an admin user password for the Graylog web interface:
echo -n "Enter Password: " && head -1
Edit the main Graylog configuration file to set the passwords:
nano /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Configure the server bind address:
http_bind_address = 127.0.0.1:9000
Start and enable the Graylog service:
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start graylog-server systemctl enable graylog-server
Check Graylog server status:
systemctl status graylog-server
Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Graylog
Install Nginx with this command:
apt install nginx -y
Create a new Nginx configuration file for Graylog:
nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/graylog.conf
Add the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name graylog.example.org;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Graylog-Server-URL http://$server_name/;
proxy_pass http://208.117.84.72:9000;
}
}
Verify Nginx configuration syntax:
nginx -t
Enable the Nginx virtual host:
ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/graylog.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Remove the default Nginx site and restart the server:
rm -rf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default systemctl restart nginx
Verify Nginx status:
systemctl status nginx
Access Graylog Web Interface
Open your web browser and navigate to http://graylog.example.com. You should see the Graylog login page:
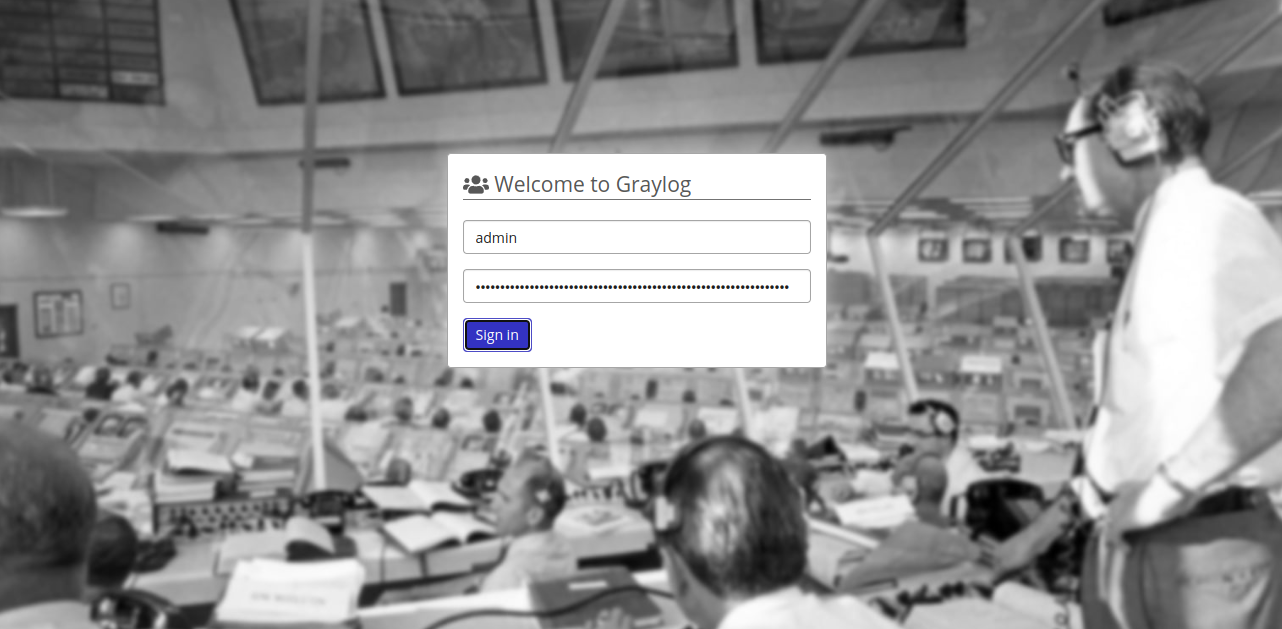
Enter your admin username and password, then click Login. You’ll be directed to the Graylog dashboard:
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed and configured Graylog with Nginx as a reverse proxy on Ubuntu 22.04. Start exploring Graylog’s features, including creating inputs to receive Rsyslog logs from external sources. Feel free to ask questions if any arise.
FAQs
- What is Graylog?
- Graylog is an open-source log management platform that helps capture, store, and analyze machine data in real-time.
- Why do I need Elasticsearch?
- Elasticsearch is used by Graylog to store logs, enabling efficient searches and log management.
- What is the role of MongoDB in Graylog?
- MongoDB stores metadata and configuration data necessary for Graylog’s operation.
- Can I use a different reverse proxy instead of Nginx?
- Yes, you can use other reverse proxies like Apache or HAProxy, though configuration steps will differ.
- How can I access Graylog’s web interface?
- You can access it via your web browser using the URL configured with your server’s domain or IP address, typically under port 9000 or as set in your reverse proxy configuration.