Effective system monitoring is vital for any system administrator to maintain optimal performance. Guider is an open-source tool designed for Linux systems to monitor and analyze system resource usage, offering insights to improve performance.
This tutorial will guide you through the installation and usage of Guider on Ubuntu 20.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 20.04.
- Root access with a configured password on your server.
Installing Guider
Guider is a Python-based tool. You need Python and PIP installed on your system. You can install them using:
apt-get install python3 python3-pip
After installing the prerequisites, install Guider with:
pip3 install --pre guider
Verify the installation by checking the version:
guider
The expected output should be:
_____ _ _
/ ____| (_) | |
| | __ _ _ _ __| | ___ _ __
| | |_ | | | | |/ _` |/ _ \ '__|
| |__| | |_| | | (_| | __/ |
\_____|\__,_|_|\__,_|\___|_| ver.3.9.8_210326 on python_3.8
Usage:
$ /usr/local/bin/guider COMMAND|FILE [OPTIONS] [--help]
Author:
Peace Lee (iipeace5@gmail.com)
Bugs:
iipeace5@gmail.com | https://github.com/iipeace/guider/issues
Copyright:
Copyright 2015-2021, Guider
License GPLv2.
This is free software
Configure Guider Buffer Size
Guider’s default buffer size might be too small. You can verify it with:
cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/buffer_size_kb
The output will appear as:
7 (expanded: 1408)
To enhance performance, set the buffer size to 40960:
echo 40960 | tee /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/buffer_size_kb
Operating Guider
To explore available options and their usage, execute:
guider --help
Review the following output with various command options:
/ G.u.i.d.e.r ver.3.9.8 /
--------------------------
Usage:
$ /usr/local/bin/guider COMMAND|FILE [OPTIONS] [--help]
COMMAND:
[CONTROL] cli
event
list
send
server
start
[LOG] logdlt
logjrl
logkmsg
logsys
printdlt
printjrl
printkmsg
printsys
[MONITOR] atop
bgtop
btop
cgtop
ctop
dbustop
disktop
dlttop
ftop
mtop
ntop
ptop
pytop
rtop
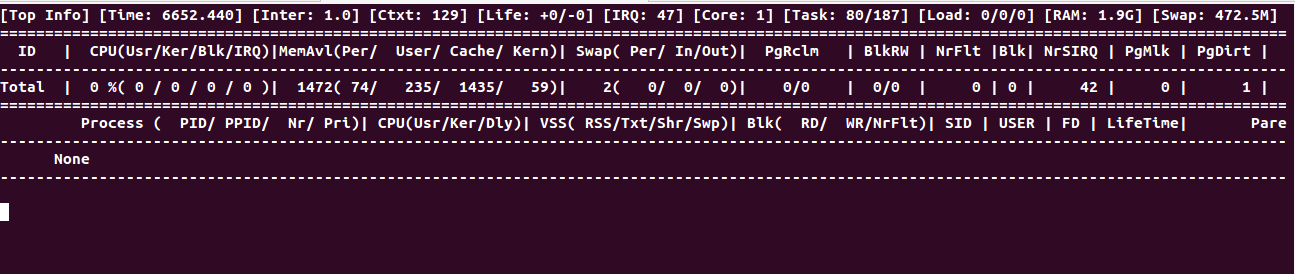
To display real-time Linux process usage, use:
guider top
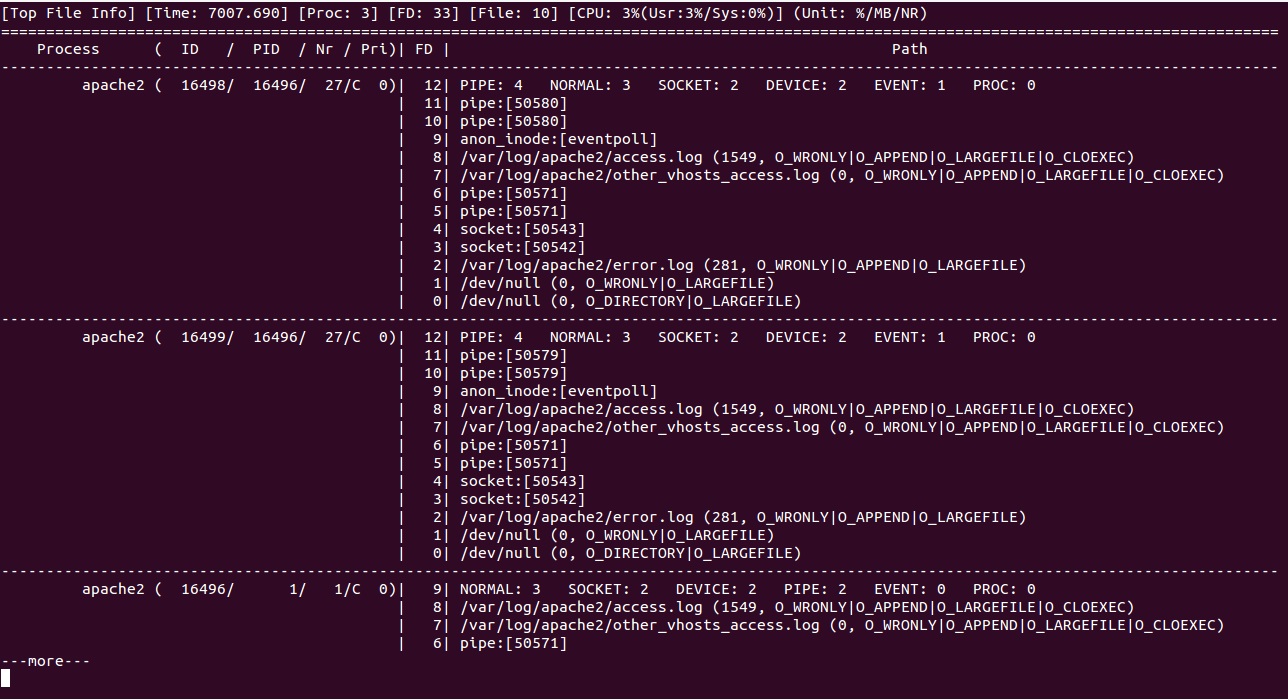
To monitor Apache process usage, execute:
guider ftop -g apache2
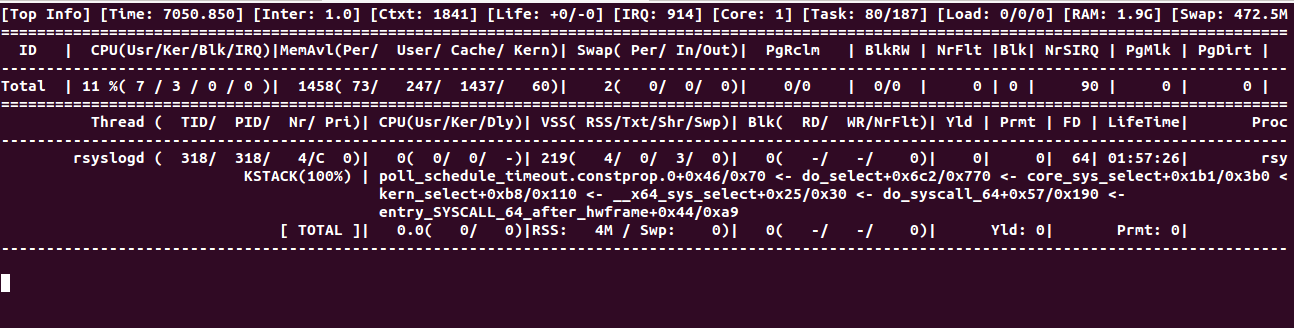
To evaluate syslog, run:
guider stacktop -g syslog
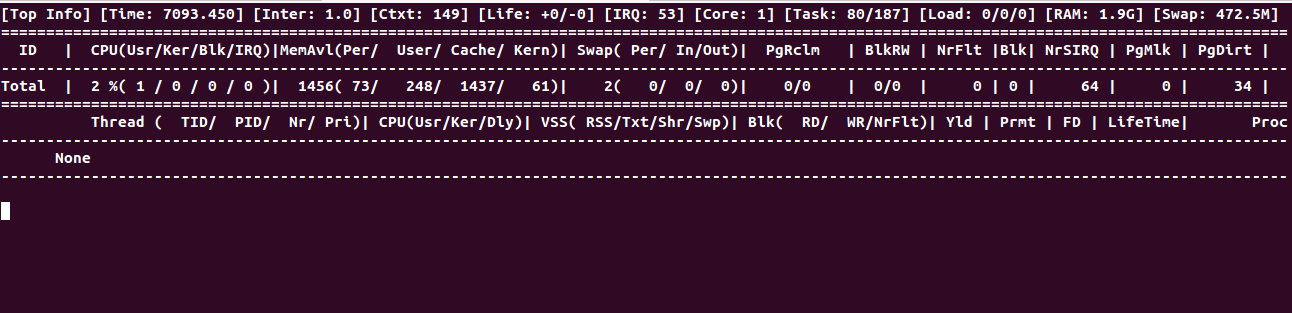
You can track real-time Memory, CPU, and Swap usage by:
guider ptop -g yes
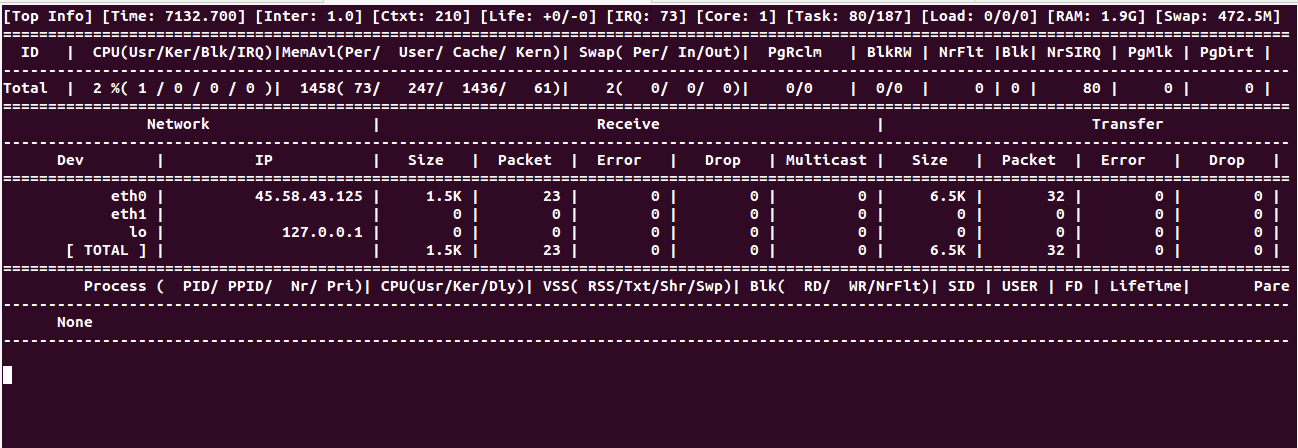
For real-time network monitoring, use:
guider ntop
To obtain systemd related details, execute:
guider printenv -g systemd
Expected output as follows:
_____ _ _ / ____| (_) | | | | __ _ _ _ __| | ___ _ __ | | |_ | | | | |/ _` |/ _ \ '__| | |__| | |_| | | (_| | __/ | \_____|\__,_|_|\__,_|\___|_| ver.3.9.8_210326 on python_3.8 [ systemd(1) ] < /sbin/init > ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- biosdevname=0 HOME=/ init=/sbin/init NETWORK_SKIP_ENSLAVED= TERM=linux BOOT_IMAGE=/boot/vmlinuz-5.4.0-29-generic drop_caps= PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin PWD=/ rootmnt=/root ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [ systemd(582) ] < /lib/systemd/systemd --user > ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- LANG=en_US.UTF-8 PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin NOTIFY_SOCKET=/run/systemd/notify HOME=/root LOGNAME=root USER=root SHELL=/bin/sh INVOCATION_ID=57fe5ba9493341f2ae3bcda335ace1ca JOURNAL_STREAM=9:17085 XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/0 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
To generate a comprehensive system analysis report, run:
guider rec -a -e m
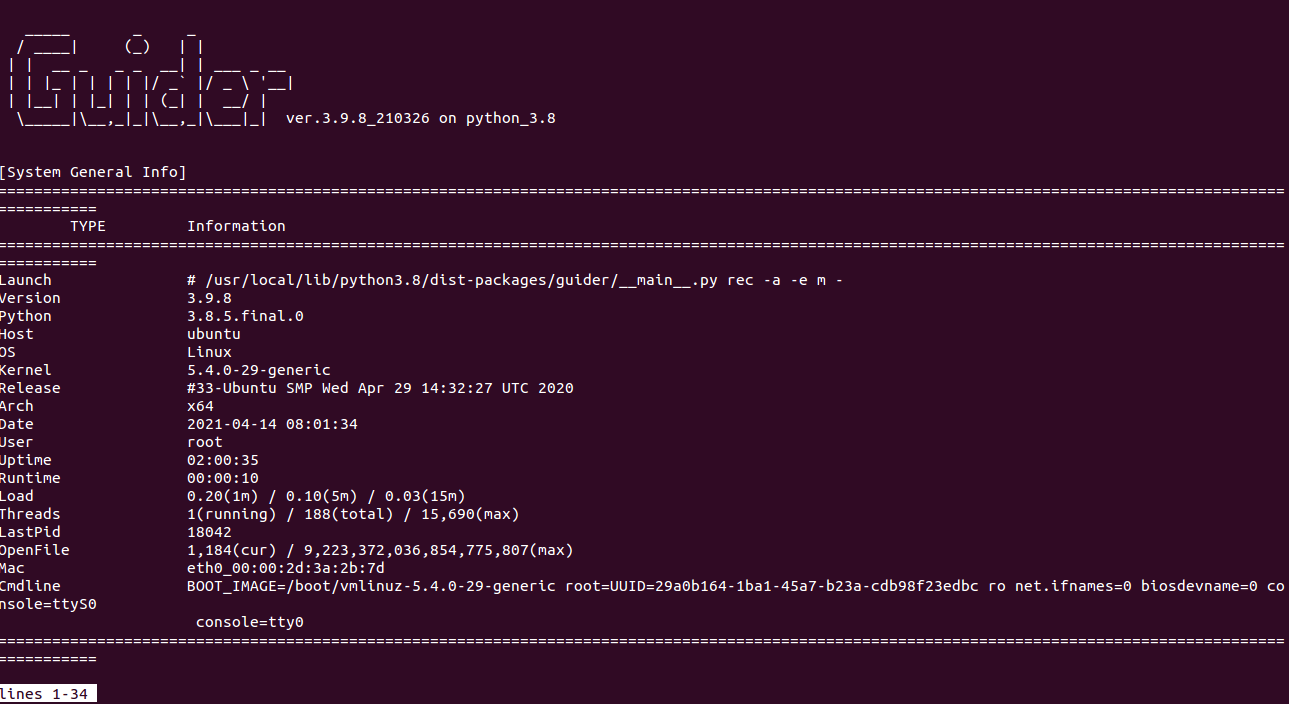
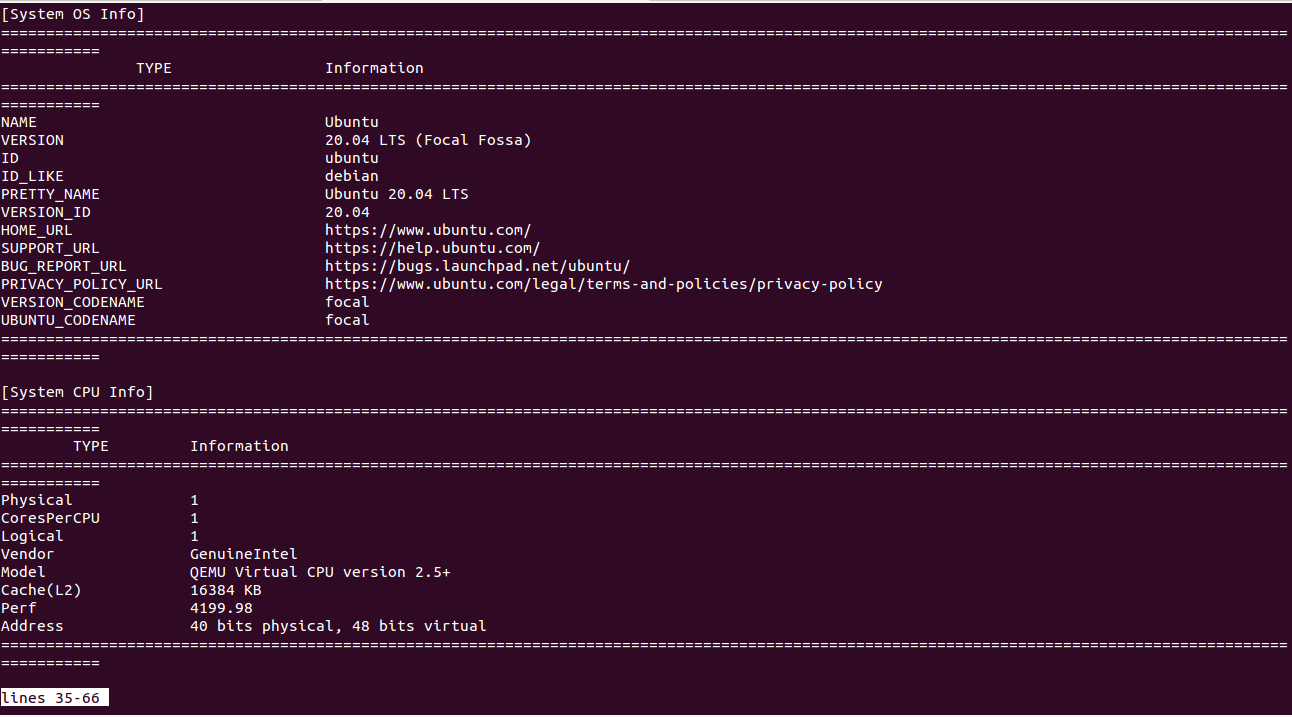
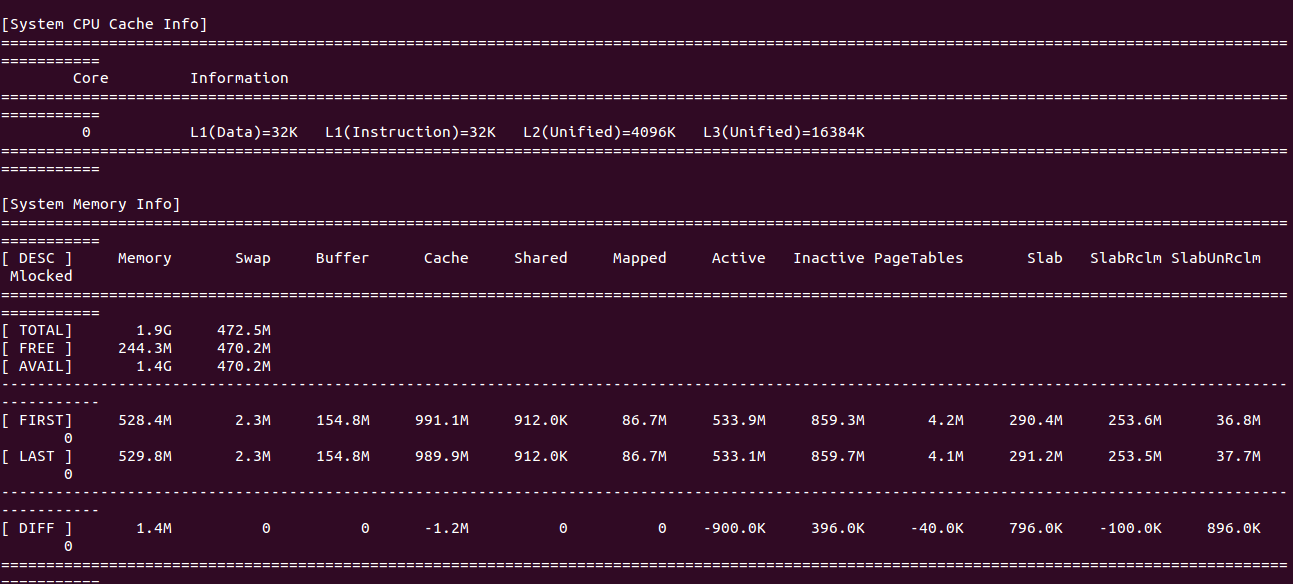
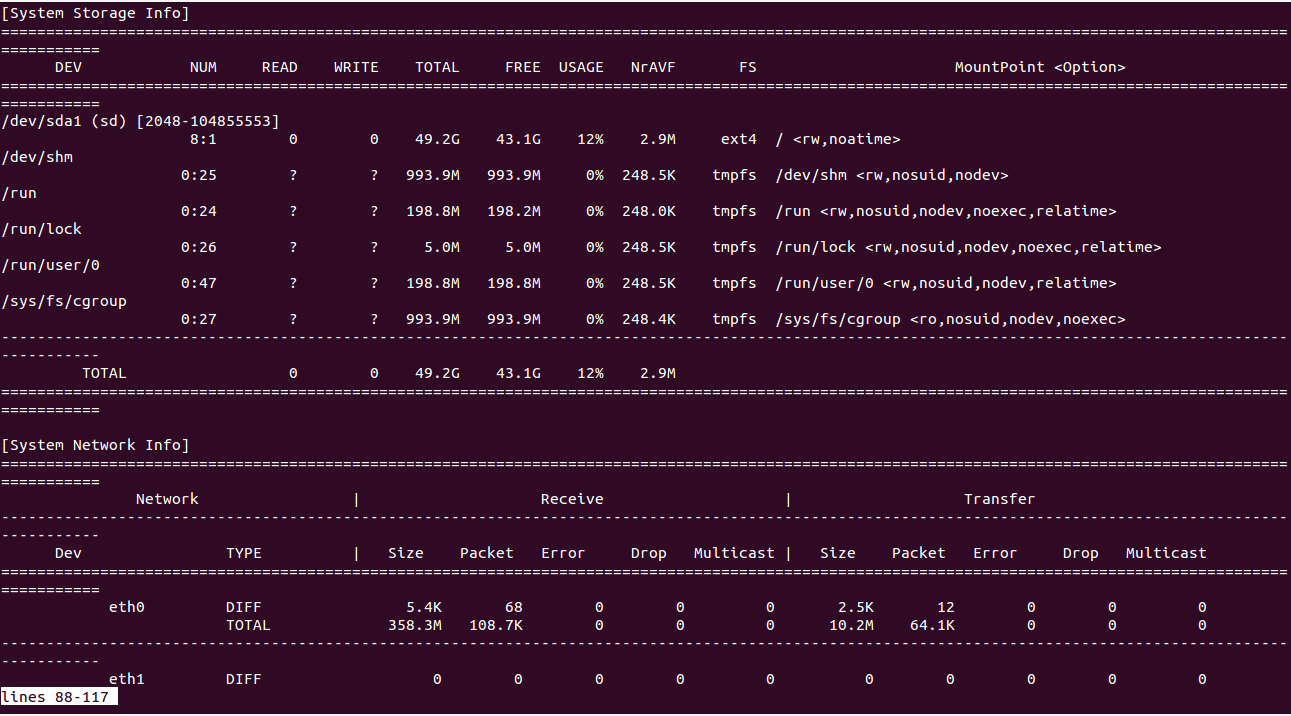
To trace the system and save it to a file, execute:
guider top -o .
This command saves the data to a file named guider.out. You can view it using:
cat guider.out
Conclusion
We’ve explored how to install and use the Guider tool for system performance analysis on Ubuntu 20.04. This robust tool can aid in optimizing your Linux system’s performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is Guider?
Guider is an open-source performance analyzer for Linux systems, used to monitor and improve system performance.
- Can I run Guider on other Linux distributions?
Yes, Guider is designed for Linux systems in general, but specific commands may vary based on the distribution.
- Does Guider support real-time monitoring?
Yes, Guider supports real-time monitoring of processes, file usage, memory, network, and more.
- Is it possible to customize the buffer size in Guider?
Yes, you can adjust the buffer size to suit your system’s needs using provided commands.
- How can I report a bug or issue with Guider?
You can report any bugs or issues by emailing iipeace5@gmail.com or raising an issue on GitHub.
