LibreNMS is a powerful monitoring tool that supports auto-discovery using multiple protocols such as SNMP, ARP, OSPF, and BGP. SNMP, available on most operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and BSDs, is commonly used for monitoring. There are three versions of the SNMP protocol: v1 and v2, secured with a community password, and v3, which supports authentication and encryption. For production environments, SNMP v3 is recommended due to its enhanced security.
In this comprehensive guide, you will learn how to install the LibreNMS monitoring tool on a Rocky Linux server. The guide includes setting up the LEMP Stack (Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP-FPM) and configuring the SNMP service to get your monitoring solution production-ready. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped to add new hosts, servers, or devices to LibreNMS for monitoring purposes.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure that you have the following:
- A Rocky Linux server (version 8 is used in this guide).
- A non-root user with sudo/administrator privileges.
- A local domain name for deployment purposes.
Setting Up Repositories
Let’s begin by setting up the necessary repositories on your Rocky Linux system, specifically the EPEL and PHP Remi repositories.
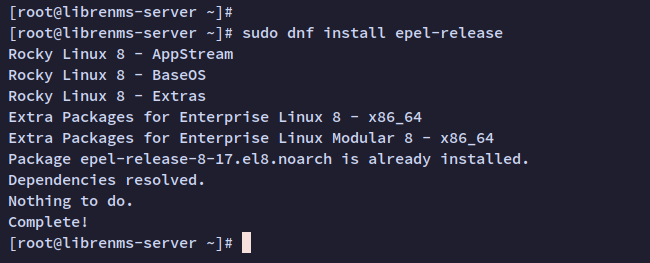
Execute the following command to add the EPEL repository:
sudo dnf install epel-release
A confirmation prompt will appear; type Y and press ENTER to continue.
Next, add the PHP Remi repository to gain access to multiple PHP versions, including the latest PHP 8.1, necessary for LibreNMS:
sudo dnf install dnf-utils http://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm
Type Y and press ENTER to proceed.
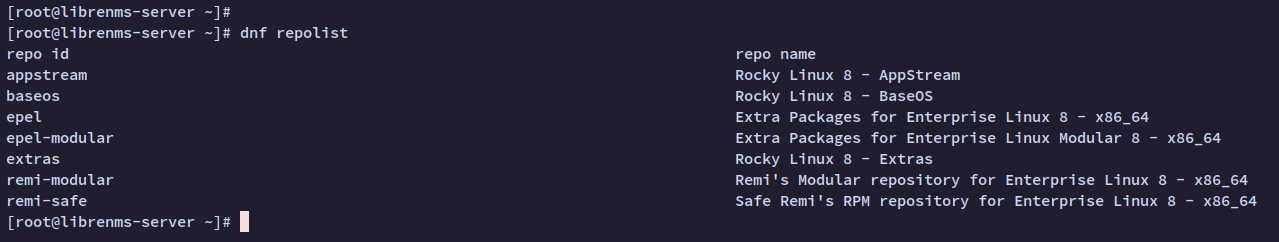
Verify the added repositories with the command below:
sudo dnf repolist
You should see listings for both the EPEL and Remi repositories.
Installing Package Dependencies
With the EPEL and Remi repositories in place, proceed to install LibreNMS’s package dependencies, which include the LEMP Stack, SNMP packages, and Python. First, enable the PHP repository module ‘remi-8.1‘ as LibreNMS requires PHP 8 or higher:
sudo dnf reset php sudo dnf module enable php:remi-8.1
Confirm by typing Y when prompted.
Install the necessary dependencies with the command below:
sudo dnf install bash-completion cronie fping git ImageMagick mariadb-server mtr net-snmp net-snmp-utils nginx nmap php-fpm php-cli php-common php-curl php-gd php-gmp php-json php-mbstring php-process php-snmp php-xml php-zip php-mysqlnd python3 python3-PyMySQL python3-devel python3-redis python3-memcached python3-pip python3-systemd rrdtool unzip
Confirm installation by typing Y and pressing ENTER.
Enable and start essential services, ensuring they run on system boot:
sudo systemctl enable nginx php-fpm mariadb snmpd sudo systemctl start nginx php-fpm mariadb snmpd
Setting up Firewalld
Ensure HTTP and HTTPS services are allowed through the firewalld firewall:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-service http sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone public --add-service https
Reload firewalld to apply these changes:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
List the active firewalld rules to ensure HTTP and HTTPS services are included:
sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
Downloading LibreNMS Source Code
Download the LibreNMS source code from GitHub and create a dedicated user ‘librenms’ to run the application.
Add the ‘librenms’ user:
sudo useradd librenms -d /opt/librenms -M -r -s "$(which bash)"
Clone the LibreNMS repository:
cd /opt git clone https://github.com/librenms/librenms.git
Set the correct ownership and permissions for the LibreNMS directory:
sudo chown -R librenms:librenms /opt/librenms sudo chmod 771 /opt/librenms
Configure access control lists for specific directories:
sudo setfacl -d -m g::rwx /opt/librenms/rrd /opt/librenms/logs /opt/librenms/bootstrap/cache/ /opt/librenms/storage/ sudo setfacl -R -m g::rwx /opt/librenms/rrd /opt/librenms/logs /opt/librenms/bootstrap/cache/ /opt/librenms/storage/
Installing PHP Dependencies for LibreNMS
Log in as the ‘librenms’ user to install PHP dependencies:
su - librenms
Execute the following script to install PHP dependencies:
./scripts/composer_wrapper.php install --no-dev
Exit the ‘librenms’ user session:
exit
Configuring PHP-FPM
Configure PHP-FPM by editing the /etc/php.ini file and ensuring the timezone is correctly set:
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Stockholm sudo nano /etc/php.ini
Find and configure the following line:
date.timezone = Europe/Stockholm
Copy the default PHP-FPM pool to create a specific pool for LibreNMS:
cp /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf /etc/php-fpm.d/librenms.conf
Edit /etc/php-fpm.d/librenms.conf and adjust the following:
[librenms] user = librenms group = librenms listen = /run/php-fpm-librenms.sock
Restart PHP-FPM to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Configuring MariaDB Server
Configure the MariaDB server and create a new database for LibreNMS. Enable the InnoDB engine before proceeding:
sudo nano /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf
Include these configurations under the ‘[mysqld]’ section:
[mysqld] innodb_file_per_table=1 lower_case_table_names=0
Restart the MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl restart mariadb
Create the LibreNMS database and user:
sudo mysql -u root -p
CREATE DATABASE librenms CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci; CREATE USER 'librenms'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON librenms.* TO 'librenms'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Verify user privileges with:
SHOW GRANTS FOR librenms@localhost;
Exit the MariaDB shell:
exit
Setting Up Nginx Server Blocks
Create a specific Nginx server block for your LibreNMS installation using your chosen domain (e.g., librenms.howtoforge.local):
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/librenms.conf
Include the following configuration:
server {
listen 80;
server_name librenms.howtoforge.local;
root /opt/librenms/html;
index index.php;
charset utf-8;
gzip on;
gzip_types text/css application/javascript text/javascript application/x-javascript image/svg+xml text/plain text/xsd text/xsl text/xml image/x-icon;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ [^/]\.php(/|$) {
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm-librenms.sock;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
include fastcgi.conf;
}
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
}
}
Check the configuration for syntax errors:
sudo nginx -t
If successful, restart Nginx:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
Configuring SELinux
To accommodate SELinux, ensure it’s set to enforcing mode and make the necessary adjustments for LibreNMS:
Install SELinux management tools:
sudo dnf install policycoreutils-python-utils
Apply file context labels for LibreNMS:
semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t '/opt/librenms/html(/.*)?' semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t '/opt/librenms/(rrd|storage)(/.*)?' semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_log_t "/opt/librenms/logs(/.*)?" semanage fcontext -a -t bin_t '/opt/librenms/librenms-service.py' restorecon -RFvv /opt/librenms chcon -t httpd_sys_rw_content_t /opt/librenms/.env
Allow necessary SELinux permissions:
setsebool -P httpd_can_sendmail=1 setsebool -P httpd_execmem 1
Prepare a custom SELinux module to allow necessary permissions:
nano http_fping.tt
Add the following content:
module http_fping 1.0;
require {
type httpd_t;
class capability net_raw;
class rawip_socket { getopt create setopt write read };
}
#============= httpd_t ==============
allow httpd_t self:capability net_raw;
allow httpd_t self:rawip_socket { getopt create setopt write read };
Compile and apply the SELinux module:
checkmodule -M -m -o http_fping.mod http_fping.tt semodule_package -o http_fping.pp -m http_fping.mod semodule -i http_fping.pp
Finishing Up the LibreNMS Configurations
Complete the setup by installing command-line utilities, configuring cron jobs, and copy logrotate settings.
Create symbolic links for ‘lnms’ command and copy bash completion scripts:
ln -s /opt/librenms/lnms /usr/bin/lnms cp /opt/librenms/misc/lnms-completion.bash /etc/bash_completion.d/
Copy default cron and logrotate configurations:
sudo cp /opt/librenms/librenms.nonroot.cron /etc/cron.d/librenms sudo cp /opt/librenms/misc/librenms.logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/librenms
Edit the SNMP configuration file:
sudo cp /opt/librenms/snmpd.conf.example /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf sudo nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Change the default community password:
# Change RANDOMSTRINGGOESHERE to your preferred SNMP community string com2sec readonly default RANDOMSTRINGGOESHERE
Save and close the file.
Download the OS detection script and set appropriate permissions:
curl -o /usr/bin/distro https://raw.githubusercontent.com/librenms/librenms-agent/master/snmp/distro chmod +x /usr/bin/distro
Restart the SNMP service to apply changes:
systemctl restart snmpd
Accessing LibreNMS Web Installation
Edit your /etc/hosts file to associate the domain with your server’s IP and access the Installer via a web browser:
192.168.5.100 librenms.howtoforge.local
Visit http://librenms.howtoforge.local/. Ensure all installation requirements are green-checked, indicating readiness for LibreNMS installation.
Click the database icon to proceed.

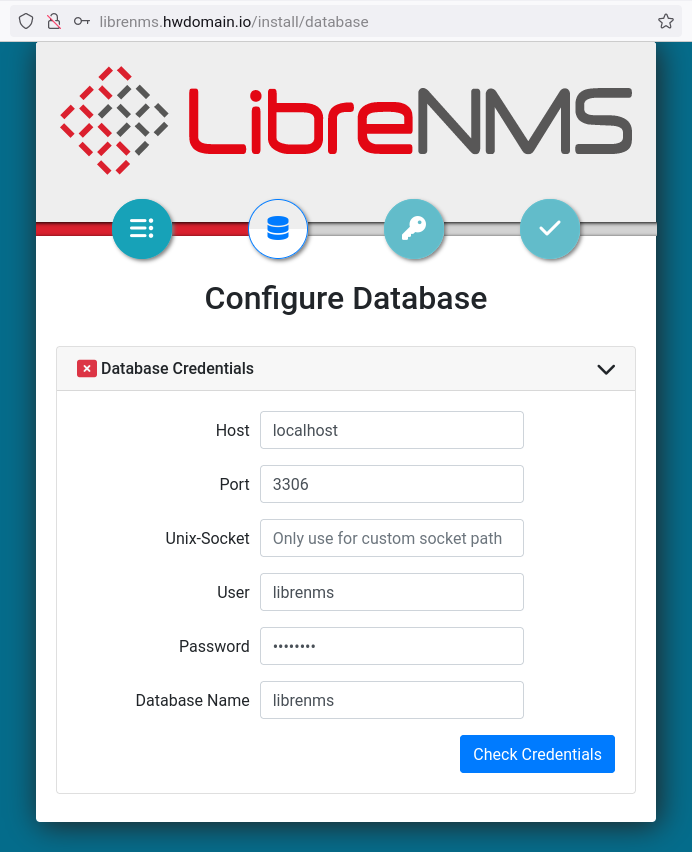
Enter database details and click “Check Credentials“.
Choose “Build Database” to initiate database migration.

After completing the database setup, configure the administrator user details and save them.


The installation is now complete, and you should see the success screen:

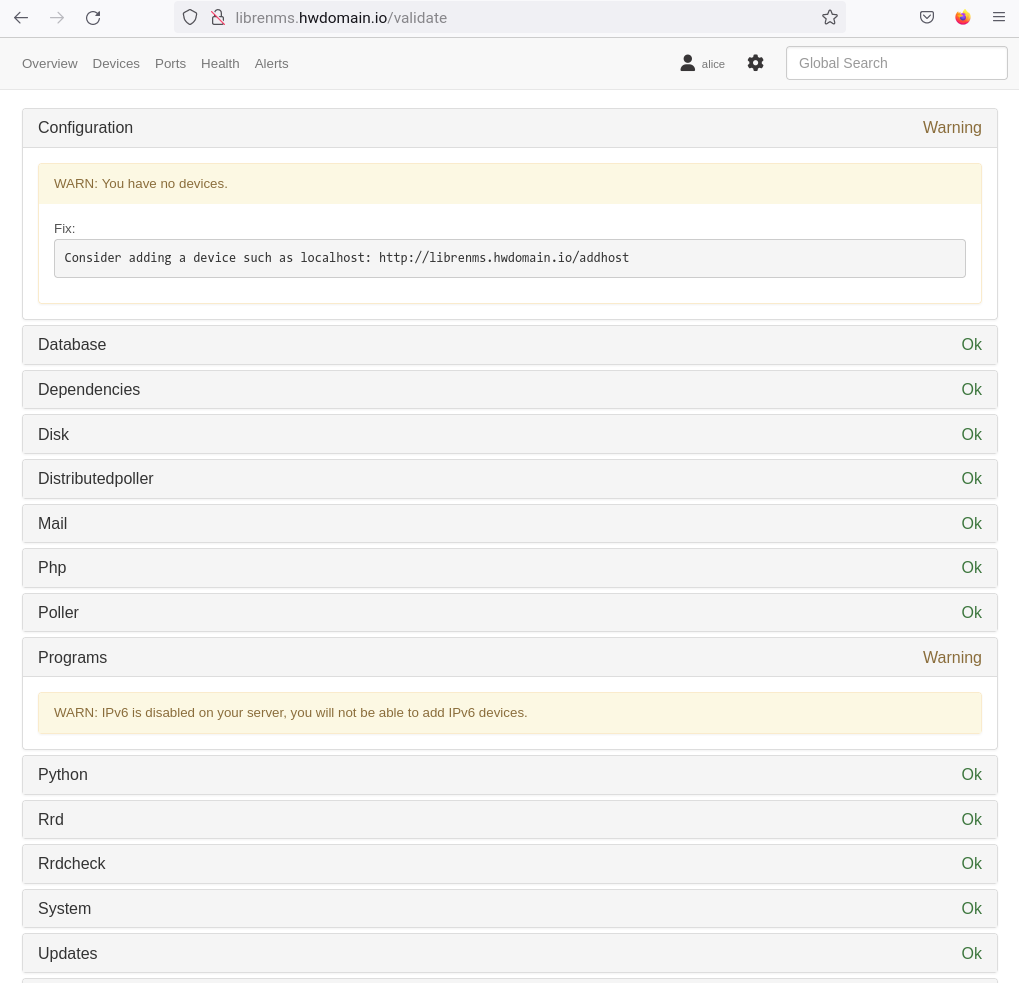
Finally, validate the installation to ensure all configurations are correct. Address any errors or warnings as suggested by LibreNMS.

Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully installed the LibreNMS Monitoring Solution on Rocky Linux. Familiarize yourself with its core features, including adding monitored hosts, configuring alerts, and integrating with third-party tools like Graylog.
FAQ
- What is LibreNMS?
- LibreNMS is an open-source network monitoring tool that supports various protocols for comprehensive network management.
- Why should I use SNMP v3 over v1 or v2?
- SNMP v3 provides enhanced security features, including authentication and encryption, making it more suitable for production environments.
- Is PHP 8.1 mandatory for LibreNMS installation?
- Yes, LibreNMS requires at least PHP 8 for installation and operation, hence the necessity for enabling the PHP Remi 8.1 repository.
- How to troubleshoot if a service doesn’t start automatically?
- Verify the service status using `systemctl status service_name` and check the error logs for detailed information.
- Where can I find more information on adding devices to monitor?
- Refer to the LibreNMS documentation and community forums for detailed guides on adding and managing monitored devices.