The LEMP software stack is a collection of open-source software used to host websites and applications on a server. LEMP stands for Linux, ENginx server, MySQL (with MariaDB), and PHP. This guide will walk you through installing a LEMP stack on a Fedora 31 server, along with PHPMyAdmin, Redis, and Opcache.
Prerequisites
- Ensure you have a server running Fedora 31.
- Have a non-root sudo user ready.
- Keep your system updated:
$ sudo dnf upgrade - Install essential packages:
$ sudo dnf install wget curl nano -yNote: These packages may already be installed.
- Disable SELinux:
$ sudo setenforce 0
Configure Firewall
Begin by configuring the firewall. Fedora includes the Firewalld firewall by default. First, verify if the firewall is running:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --stateYou should see:
runningSet the default firewall zone to public:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=publicCheck the current services/ports allowed:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --list-servicesExpected output:
dhcpv6-client mdns sshAdd HTTP and HTTPS services:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=http
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=httpsCheck the updated firewall settings:
$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --list-servicesNew output should be:
dhcpv6-client http https mdns sshReload the firewall settings:
$ sudo systemctl reload firewalldInstall PHP
Fedora 31 supports PHP 7.3 natively, but PHP 7.4 is preferred. Add the REMI repository:
$ sudo dnf -y install https://rpms.remirepo.net/fedora/remi-release-31.rpmEnable the appropriate repositories and disable the modular repository:
$ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled remi
$ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled remi-php74
$ sudo dnf config-manager --set-disabled remi-modularInstall PHP 7.4 and additional packages:
$ sudo dnf install -y php-cli php-fpm php-mysqlndVerify PHP installation:
$ php --versionExpected output:
PHP 7.4.3 (cli) (built: Feb 18 2020 11:53:05) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend TechnologiesInstall MariaDB
MariaDB acts as a drop-in replacement for MySQL. Fedora 31 includes MariaDB 10.3 but we’ll set up version 10.4. Create a new repository file:
$ sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repoAdd this content:
# MariaDB 10.4 Fedora repository list
# http://downloads.mariadb.org/mariadb/repositories/
[mariadb]
name = MariaDB
baseurl = http://yum.mariadb.org/10.4/fedora31-amd64
gpgkey=https://yum.mariadb.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDB
gpgcheck=1Install MariaDB server:
$ sudo dnf install MariaDB-server -yVerify MariaDB installation:
$ mysql --versionExpected output:
mysql Ver 15.1 Distrib 10.4.12-MariaDB, for Linux (x86_64) using EditLine wrapperEnable and start MariaDB:
$ sudo systemctl enable mariadb
$ sudo systemctl start mariadbSecure the installation:
$ sudo mysql_secure_installationInstall Nginx
Fedora 31 comes with Nginx 1.16.1. Install it by running:
$ sudo dnf install nginx -yVerify Nginx installation:
$ nginx -vExpected output:
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1Start and enable Nginx:
$ sudo systemctl start nginx
$ sudo systemctl enable nginxVisit your server’s IP in a browser to see Nginx’s test page.
Configure Nginx
Create directories for server blocks:
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-available
$ sudo mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-enabledCreate a directory for your site:
$ sudo mkdir /var/www/example.com/html -pAdd a configuration file for your site:
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.confInsert the following configuration:
server {
listen *:80;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/html;
index index.php index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/example.com.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/example.com.error.log;
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}Link this configuration to sites-enabled:
$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/Edit the main Nginx configuration:
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.confAdd these lines:
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*.conf;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;Modify types_hash_max_size:
types_hash_max_size 4096;Save your changes, then test the Nginx configuration:
$ sudo nginx -tReload Nginx:
$ sudo systemctl reload nginxConfigure PHP-FPM
Edit PHP-FPM configuration file:
$ sudo nano /etc/php-fpm.d/www.confChange the user and group to nginx:
user = nginx
group = nginxSet permission for the Unix socket:
listen.owner = nginx
listen.group = nginxRestart PHP-FPM:
$ sudo systemctl restart php-fpmCreate a test.php in the html folder:
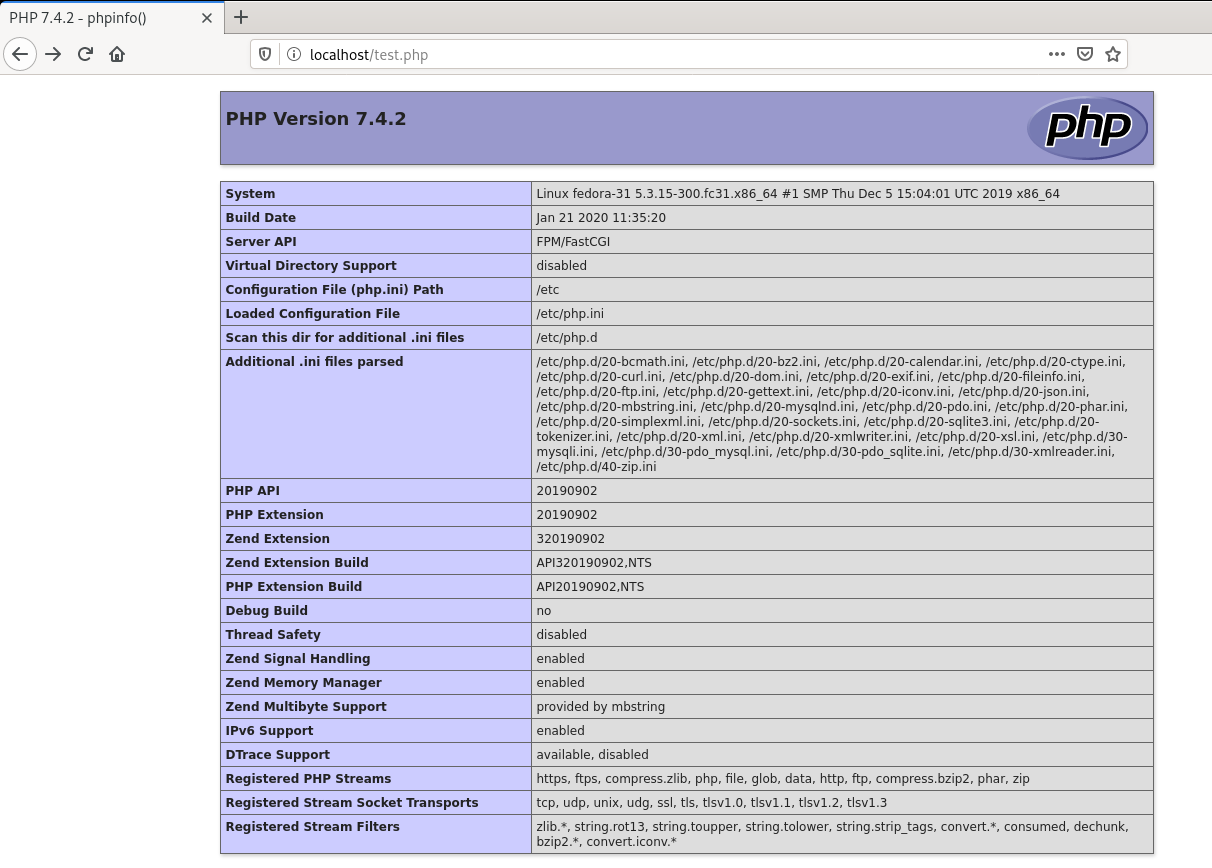
$ sudo nano /var/www/example.com/html/test.phpAdd this code and save:
<?php phpinfo();Visit http://<yourserverip>/test.php to verify PHP setup.
Conclusion
You have successfully set up a LEMP stack on your Fedora 31 server. Begin developing and hosting your websites and applications!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Why use the REMI repository?The REMI repository provides newer versions of PHP than the default Fedora repositories, giving access to performance improvements and new features.
- What is the benefit of using MariaDB over MySQL?MariaDB is an improved, drop-in replacement for MySQL. It provides better performance and additional features while maintaining compatibility.
- Can I use a different version of PHP?Yes, you can use different PHP versions available in the repositories or compile from source code, though it may involve additional steps in configuration.
- How can I enable SELinux?To re-enable SELinux, change its status with
sudo setenforce 1and ensure SELinux policies are set appropriately for your server services. - What if I encounter permission errors?If you face permission issues, ensure that file and directory permissions are set correctly, especially for the web server and PHP-FPM processes.
