SaltStack, an open-source IT automation framework, is designed for efficient remote command execution across multiple machines. Written in Python, it operates on a Master and Minion architecture. The Salt Master serves as the central control for configuration management, while Minions are the servers managed by the Master.
This guide will walk you through the process of installing SaltStack on Debian 12 servers. We will cover the installation of both the Salt Master and Minion, demonstrate running arbitrary commands using Salt, and illustrate how to create a Salt state for LAMP Stack installation.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have the following before beginning:
- Two or three Debian 12 servers. For this example, we use a master server at 192.168.5.15 and a minion1 server at 192.168.5.21.
- A non-root user with administrative privileges.
Configuring the /etc/hosts File
First, configure the /etc/hosts file so that each server can connect via hostname, offering more straightforward management than using IP addresses.
Open the /etc/hosts file with the nano editor:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Add your server details into the file accordingly. Update the IP addresses and hostnames as needed:
192.168.5.15 master 192.168.5.21 minion1
Save and exit the file.
Adding the SaltStack Repository
Next, incorporate the SaltStack repository across your Debian servers. SaltStack’s official repository covers many Linux distributions, including Debian 12.
Create a new directory for keyrings:
mkdir /etc/apt/keyrings
Download the GPG key for the SaltStack repository:
sudo curl -fsSL -o /etc/apt/keyrings/salt-archive-keyring-2023.gpg https://repo.saltproject.io/salt/py3/debian/12/amd64/SALT-PROJECT-GPG-PUBKEY-2023.gpg
Add the SaltStack repository:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/salt-archive-keyring-2023.gpg arch=amd64] https://repo.saltproject.io/salt/py3/debian/12/amd64/latest bookworm main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/salt.list
Update the Debian package index:
sudo apt update
Configuring UFW
Set up and enable the Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) on your Debian servers to maintain secure SSH connections.
Install UFW:
sudo apt install ufw -y
Allow the OpenSSH profile:
sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
Enable UFW and confirm the activation:
sudo ufw enable
Installing Salt Master
With the preliminary steps completed, proceed to install SaltStack. Begin by configuring the Salt Master on the master server.
Install the salt-master package:
sudo apt install salt-master
Edit the Salt Master’s configuration to set its local IP address:
sudo nano /etc/salt/master
Replace the default interface with:
interface: 192.168.5.15
Save and close the file.
Apply the changes by restarting the salt-master service:
sudo systemctl restart salt-master
Verify the salt-master service is running:
sudo systemctl status salt-master
Look for the status ‘active (running)‘.
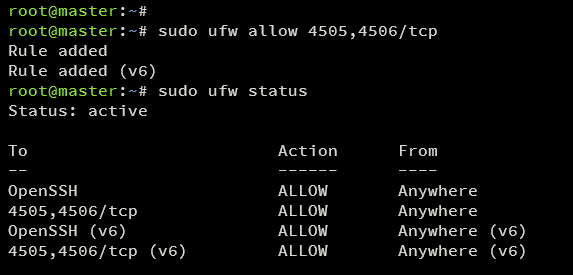
Open necessary TCP ports for Salt Master:
sudo ufw allow 4505,4506/tcp
Verify port access:
sudo ufw status
Installing Salt Minion
Next, set up the Salt Minion on the minion1 server. This will allow it to communicate with the Salt Master.
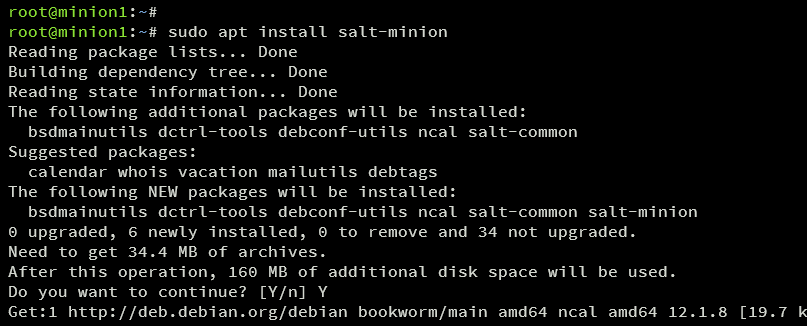
Install the salt-minion package:
sudo apt install salt-minion
Edit the Salt Minion configuration to connect to the Salt Master:
sudo nano /etc/salt/minion
Set the master parameter:
master: 192.168.5.15
Save and exit.
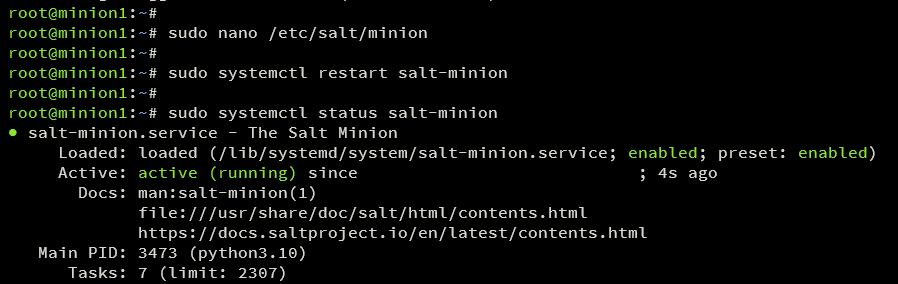
Restart the salt-minion service:
sudo systemctl restart salt-minion
Verify the salt-minion service is up and running:
sudo systemctl status salt-minion
The Salt Minion should automatically connect to the Salt Master.
Adding Salt Minion to Salt Master
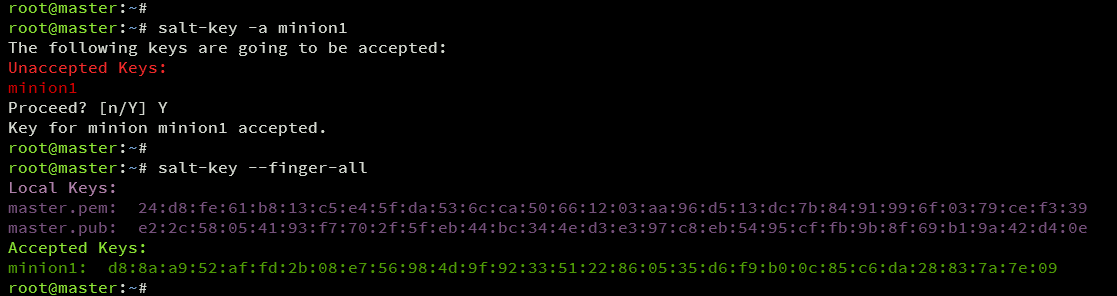
After configuring the Salt Minion, accept its registration key on the Salt Master.
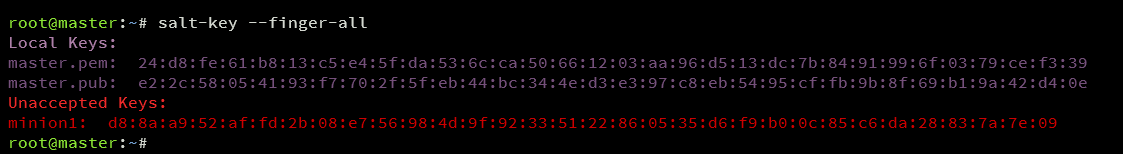
List the current keys on the master server:
salt-key --finger-all
View the key for the minion1 server.
Accept the key for the minion1 server:
salt-key -a minion1
Re-check key listings:
salt-key --finger-all
The key for minion1 should now appear in Accepted Keys.
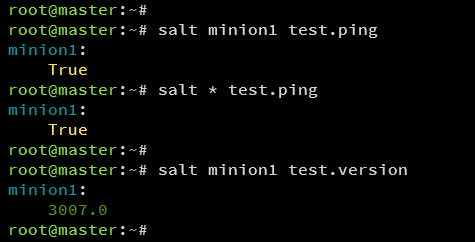
Test the connection to the Salt Minion:
salt minion1 test.ping salt * test.ping
Successful connection will return ‘True‘.
Verify the Salt version:
salt minion1 test.version
Example output suggests Salt Minion 3007.0 is installed.
Executing Arbitrary Commands with SaltStack
With configuration complete, use SaltStack to run arbitrary commands on the minion1 server from the master:
Update package index on Minion servers:
salt '*' pkg.refresh_db
List available package upgrades:
salt '*' pkg.list_upgrades
Display information about the apache2 package:
salt '*' pkg.show apache2
Check running services on the Minion:
salt '*' service.get_running salt '*' service.execs
Creating a Salt State for LAMP Stack Installation
To deploy a LAMP Stack (Apache, MariaDB, and PHP) on the minion1 server, follow this guide on creating a SaltState.
Create a new directory:
mkdir -p /srv/salt/lamp
Create an init file for the Salt state:
nano /srv/salt/lamp/init.sls
Insert the configuration below for LAMP installation:
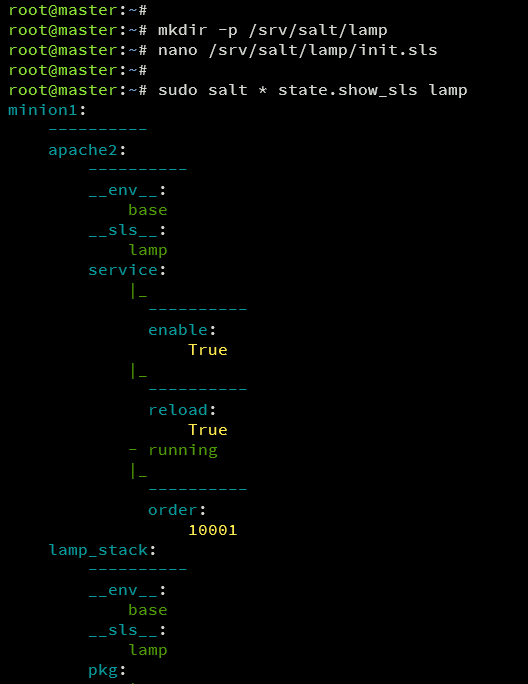
lamp_stack: pkg.installed: - pkgs: - apache2 - mariadb-server - php - libapache2-mod-php apache2: service.running: - enable: True - reload: True mariadb: service.running: - enable: True - reload: True
Save and close.
Verify the configuration:
sudo salt * state.show_sls lamp
Apply the Salt state to the minion1 server:
sudo salt minion1 state.apply lamp
The process will conclude with a success message:
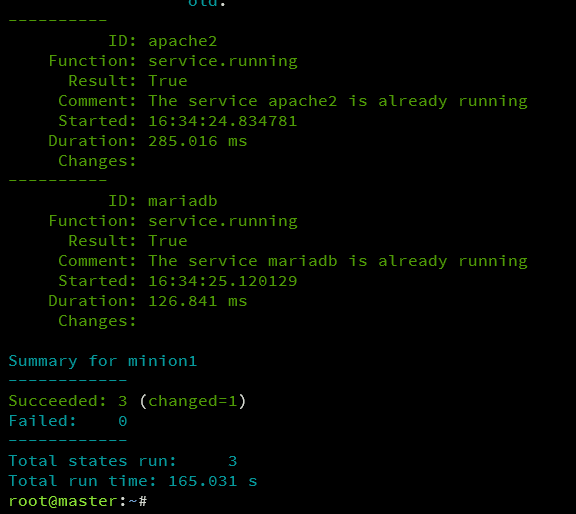
Check that Apache and MariaDB services are running:
salt '*' service.get_running
Both services, apache2, and mariadb, should be active.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully installed SaltStack (both Master and Minion) on Debian 12 servers. You’ve also learned how to execute arbitrary commands on Minion servers and created a Salt state for deploying a LAMP Stack comprising Apache, MariaDB, and PHP.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is SaltStack?
- SaltStack is an open-source IT automation framework designed for remote command execution and configuration management across multiple machines.
-
Why use Master and Minion architecture in SaltStack?
- The Master and Minion architecture allows a central server (Master) to manage, control, and push configurations to numerous clients (Minions), making management scalable and efficient.
-
What are the system requirements for installing SaltStack?
- The minimum requirements are a system running Debian 12, with a non-root user having administrative privileges. SaltStack itself does not impose additional heavyweight requirements.
-
How do I trust a Salt Minion?
After configuring Salt Minion, the Master needs to accept the Minion’s registration key using the
salt-key -a {minion_id}command. -
Can I execute commands asynchronously using SaltStack?
- Yes, SaltStack allows you to run commands asynchronously, which helps in executing tasks without waiting for completion, making the process more efficient.
-
What can I achieve with Salt states?
- Salt states allow you to define the desired state configurations for systems, automating tasks like package installations, service management, and even user management.
