File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is one of the oldest and most well-known network protocols available. While not as secure as modern alternatives like SFTP or SCP due to its lack of encryption for data and user credentials, FTP remains a popular choice for many users who need to transfer files between a server and a client. Despite these security considerations, FTP’s simplicity and broad platform support keep it in demand.
Among the plethora of open-source FTP servers available today—such as FTPD, ProFTPD, and Pure-FTPd—VSFTPD stands out as a particularly secure, fast, and widely used solution for file transfers. Known as the “Very Secure File Transfer Protocol Daemon,” VSFTPD supports SSL, IPv6, and both explicit and implicit FTPS, offering enhanced security features.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of installing the VSFTPD FTP server on a Debian 11 system.
Prerequisites
- A server running Debian 11
- A non-root user with sudo privileges
1. Install Vsftpd
First, update your Debian 11 server by executing the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt upgrade -y
Since Debian’s repository includes the VSFTPD package, installation is straightforward. Use the following command to install VSFTPD:
sudo apt install vsftpd -y
After installing the package, start the VSFTPD service, verify its status, and enable it to run at startup:
sudo systemctl start vsftpd
sudo systemctl status vsftpd
systemctl enable vsftpd.service
2. Create an FTP User and Configure for FTP Login
Create a new user account that will be used to log in to the FTP server:
sudo adduser sohan
The user needs permission to access the FTP server, so add the user to the vsftpd user list:
echo "sohan" | sudo tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist
3. Create FTP User Directory
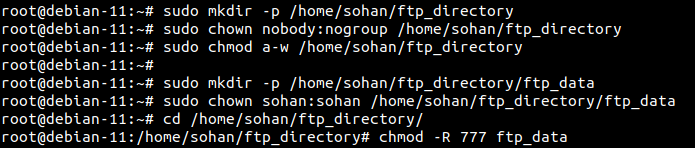
Now, create an FTP directory for your FTP user and set appropriate ownership and permissions:
sudo mkdir -p /home/sohan/ftp_directory
sudo chown nobody:nogroup /home/sohan/ftp_directory
sudo chmod a-w /home/sohan/ftp_directory
Then, create a directory for uploading files and grant ownership to the user:
sudo mkdir -p /home/sohan/ftp_directory/ftp_data
sudo chown sohan:sohan /home/sohan/ftp_directory/ftp_data
cd /home/sohan/ftp_directory/
chmod -R 777 ftp_data
4. Configure Vsftpd
It’s necessary to change some default parameters to properly set up your FTP server. First, back up the original VSFTPD configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd.conf.bak
By default, anonymous users are granted access to the FTP server. To enhance security, we will disable anonymous logins:
Open the vsftpd.conf file and make the following changes:
vim /etc/vsftpd.conf
anonymous_enable=NO
local_enable=YES
Add the following lines to the vsftpd.conf file, adjusting as needed:
listen=NO
listen_ipv6=YES
anonymous_enable=NO
write_enable=YES
local_umask=022
dirmessage_enable=YES
use_localtime=YES
xferlog_enable=YES
connect_from_port_20=YES
chroot_local_user=YES
secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty
pam_service_name=vsftpd
user_sub_token=$USER
local_root=/home/$USER/ftp_directory
userlist_enable=YES
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist
userlist_deny=NO
Save and close the file. Now, restart the VSFTPD service and check its status:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
sudo systemctl status vsftpd
5. Allow Vsftpd in Firewall and Access the Vsftpd Server
If a firewall is in place, allow ports 21 and 22 with these commands:
sudo ufw allow 21/tcp
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp
Reload the firewall to apply changes:
sudo ufw reload
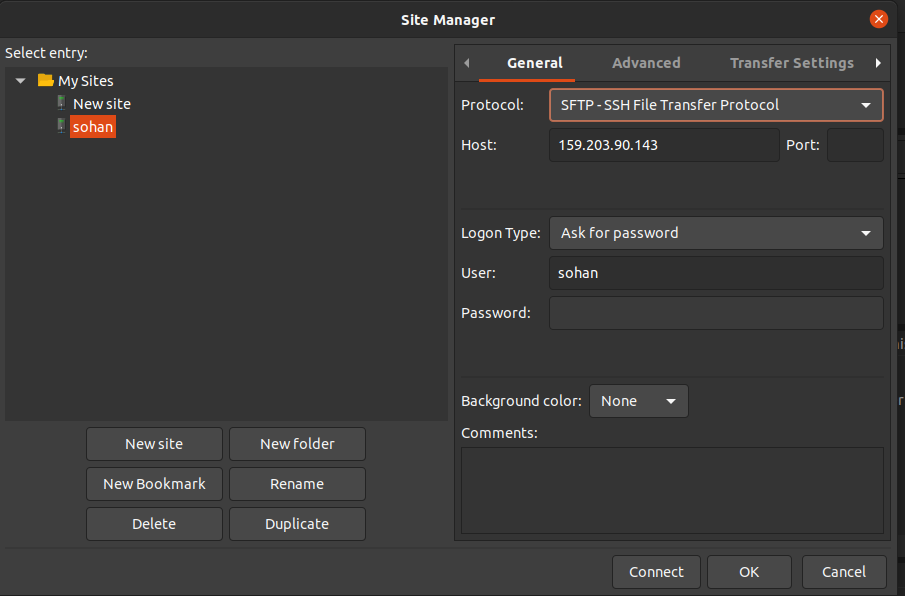
Use an FTP client like FileZilla, entering your server’s details such as Protocol, Host, and User:
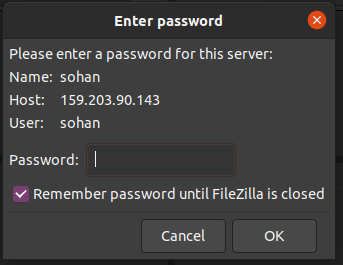
Click on connect and then enter your password:
Accept the connection details by clicking OK:
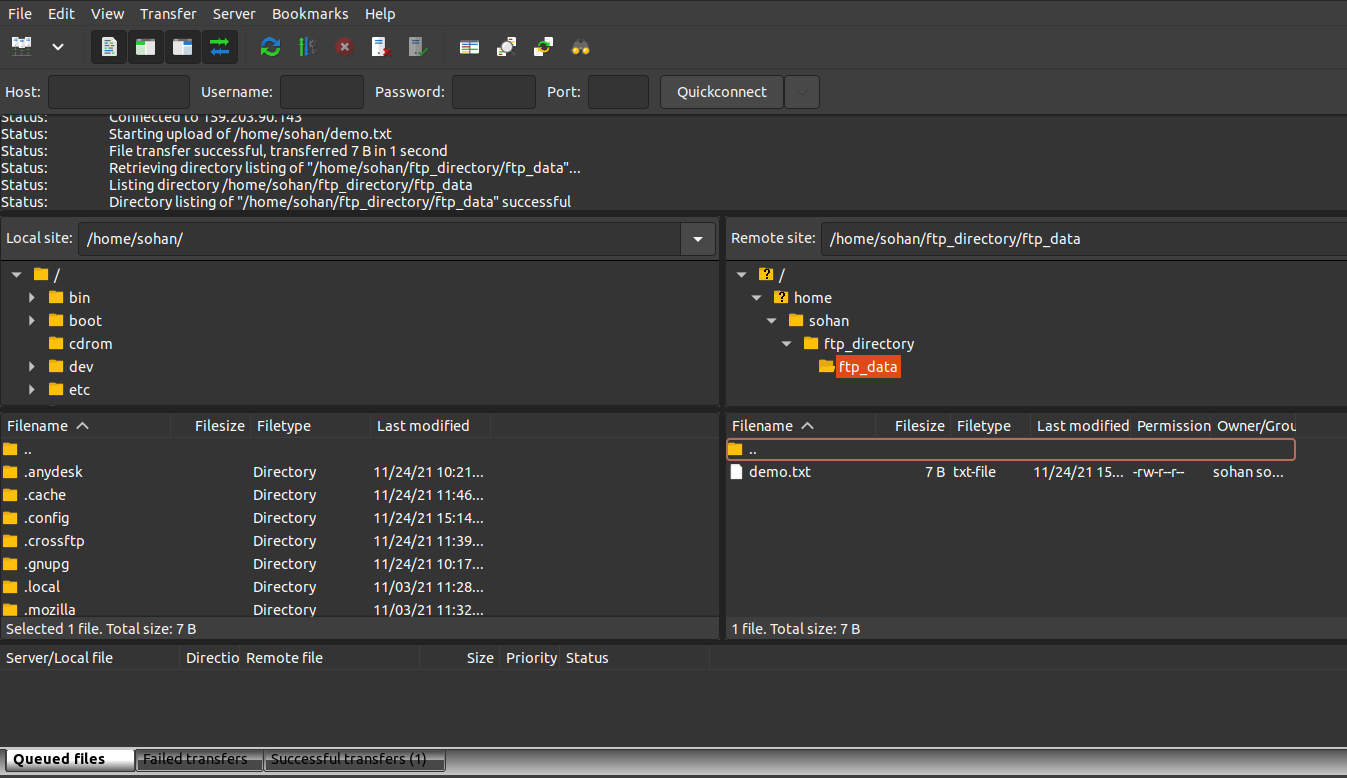
You are now connected to the FTP server and can begin transferring files:
6. Secure Vsftpd Using SSL/TLS
To transfer encrypted data via FTP, create an SSL certificate and enable SSL/TLS connections:
Generate a certificate with OpenSSL using this command:
sudo mkdir /etc/cert
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/cert/vsftpd.pem -out /etc/cert/vsftpd.pem
Edit the vsftpd.conf file and add the following lines:
sudo vim /etc/vsftpd.conf
rsa_cert_file=/etc/cert/vsftpd.pem
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/cert/vsftpd.pem
ssl_enable=YES
allow_anon_ssl=NO
force_local_data_ssl=YES
force_local_logins_ssl=YES
ssl_tlsv1=YES
ssl_sslv2=NO
ssl_sslv3=NO
require_ssl_reuse=NO
ssl_ciphers=HIGH
Save and exit the file. Restart Vsftpd:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
7. Access FTP Over SSL/TLS
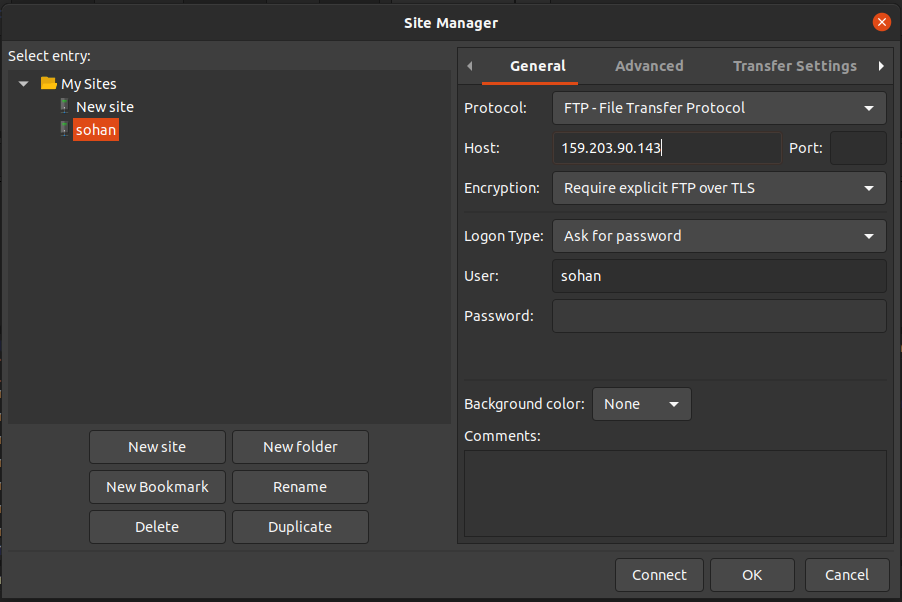
Use FileZilla to securely connect: go to File > Site Manager, create a new site, and enter details such as the host, protocol, and encryption options. Choose “Require explicit FTP over TLS” for encryption, then click Connect:
Enter your password:
Verify the SSL certificate details and click OK to proceed:
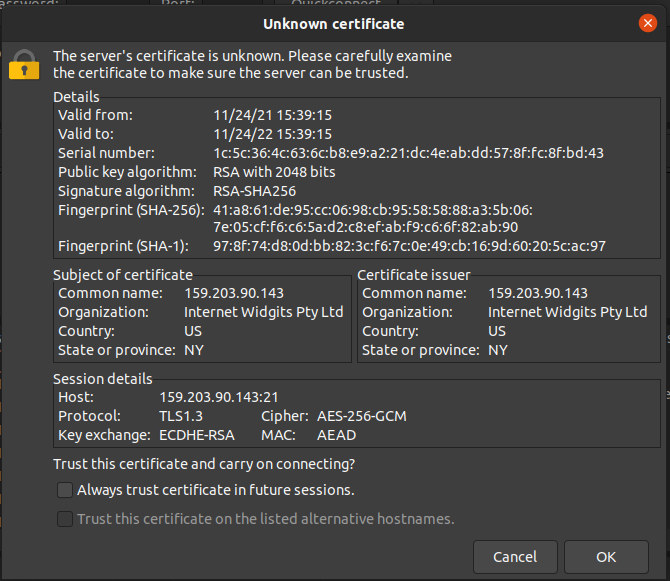
You can now securely transfer your data:
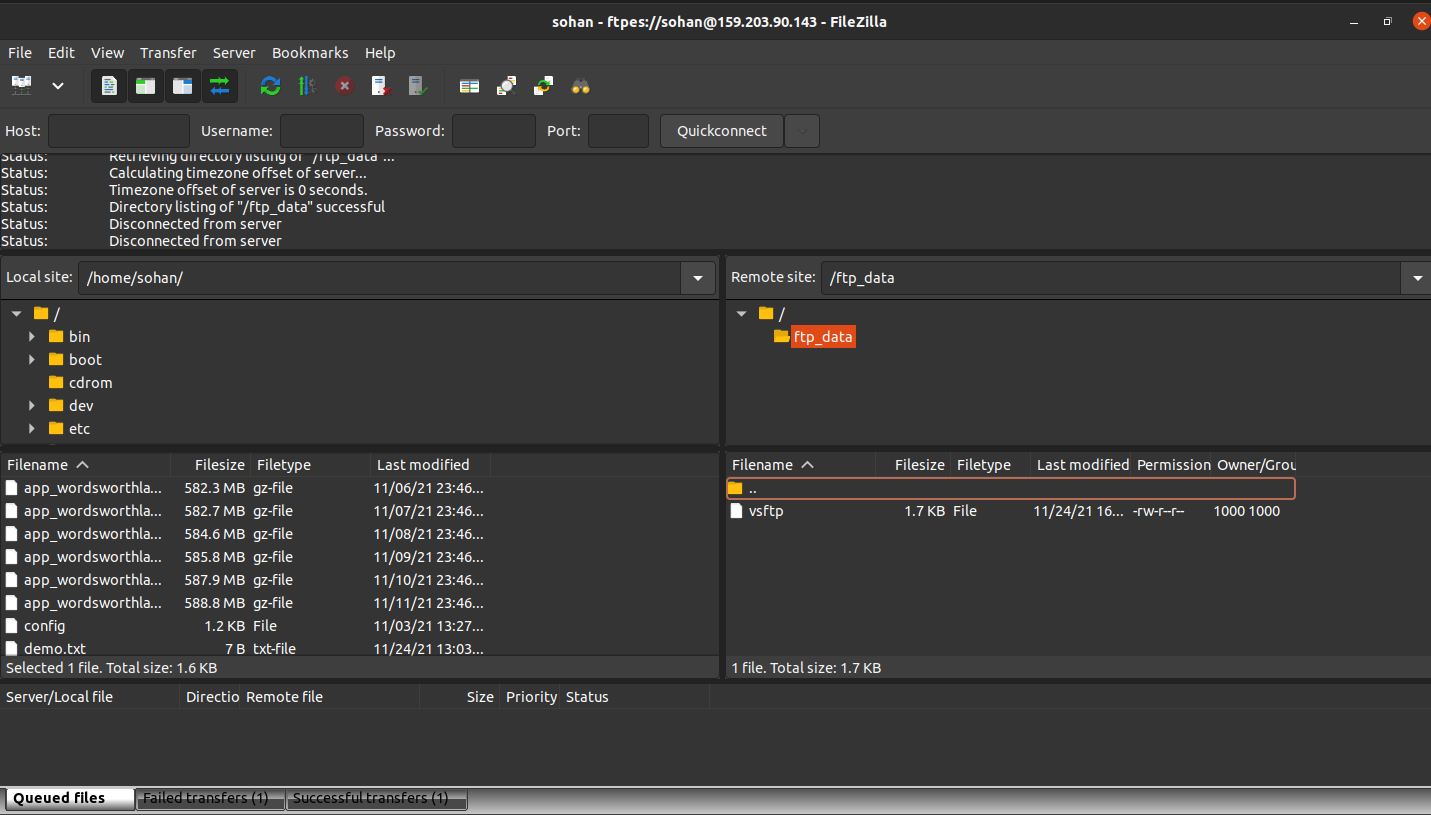
Conclusion
This guide covered the installation of the VSFTPD FTP server on Debian 11. We configured connections for both unencrypted and encrypted (SSL/TLS) transfers, enabling you to securely transfer your files.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between FTP and VSFTPD?
FTP is a protocol for transferring files, while VSFTPD (Very Secure FTP Daemon) is a specific FTP server that implements FTP and FTPS, known for its speed and security features.
2. Why should I use VSFTPD instead of other FTP servers?
VSFTPD is known for its security, performance, and configurability, supporting SSL/TLS, which encrypts connections and enhances security.
3. Can I use VSFTPD with SELinux enabled?
Yes, but you’ll need to adjust SELinux policies to allow VSFTPD to function correctly. This can be done using SELinux management tools to configure vsftpd permissions.
4. How can I add additional users to the VSFTPD server?
Create a new user using the ‘adduser’ command and add them to the /etc/vsftpd.userlist file to grant FTP access.
5. What should I do if I experience permission issues?
Check directory ownership and permissions to ensure they are correctly set for the user’s FTP directory and attempt to connect.