Docker Compose is an invaluable tool that simplifies the management of complex applications by allowing you to define and orchestrate multiple containers with a single service. It utilizes a YAML file where you can specify the different services that make up your application, focusing on development, testing, and staging environments.
This guide will walk you through the process of installing and using Docker Compose on a CentOS 8 server.
Requirements
- A server running CentOS 8.
- A root password configured on the server.
Install Docker
First, ensure Docker is installed on your server. If Docker is not already installed, add the Docker-CE repository to your system with the command below:
dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
With the repository added, install the latest version of Docker using:
dnf install docker-ce --nobest -y
systemctl start docker systemctl enable docker
Verify your Docker installation with:
docker --version
Expected output:
Docker version 19.03.5, build 633a0ea
Install Docker Compose
Docker Compose is not available in the default CentOS 8 repository, so you need to download it from the official GitHub repository.
First, install the curl command if it is not already installed:
dnf install curl -y
Use curl to download the latest Docker Compose version:
curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.25.0/docker-compose-`uname -s`-`uname -m` -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
After downloading, make it executable:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
Verify the installation:
docker-compose --version
Expected output:
docker-compose version 1.25.0, build 0a186604
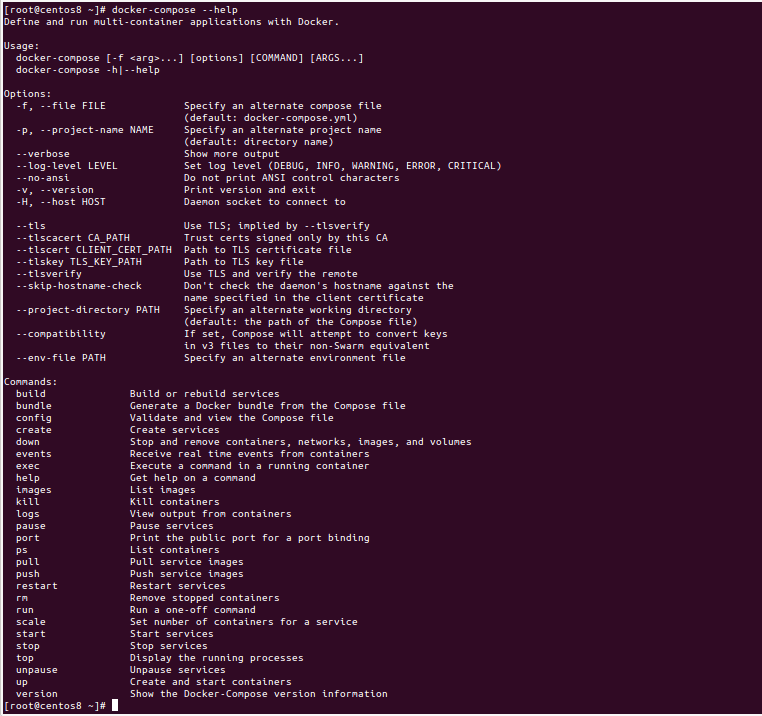
List all available Docker Compose options:
docker-compose --help
Deploy Drupal with Docker Compose
Next, we will demonstrate how to deploy Drupal with Docker Compose.
Create a directory for your Drupal setup:
mkdir drupal
Create a docker-compose.yaml file inside this directory:
nano drupal/docker-compose.yaml
Insert the following configuration:
version: '3.3'
services:
drupal:
image: drupal:latest
ports:
- 80:80
volumes:
- drupal_modules:/var/www/html/modules
- drupal_profiles:/var/www/html/profiles
- drupal_themes:/var/www/html/themes
- drupal_sites:/var/www/html/sites
restart: always
postgres:
image: postgres:10
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: your_postgres_password
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
restart: always
volumes:
drupal_modules:
drupal_profiles:
drupal_themes:
drupal_sites:
db_data:
Save and close the file when done. Navigate to the Drupal directory and launch the containers:
cd drupal docker-compose up -d
Your Drupal and PostgreSQL containers will start downloading and running.
To check the running containers:
docker-compose ps
Expected output:
Name Command State Ports ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- drupal_drupal_1 docker-php-entrypoint apac ... Up 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp drupal_postgres_1 docker-entrypoint.sh postgres Up 5432/tcp
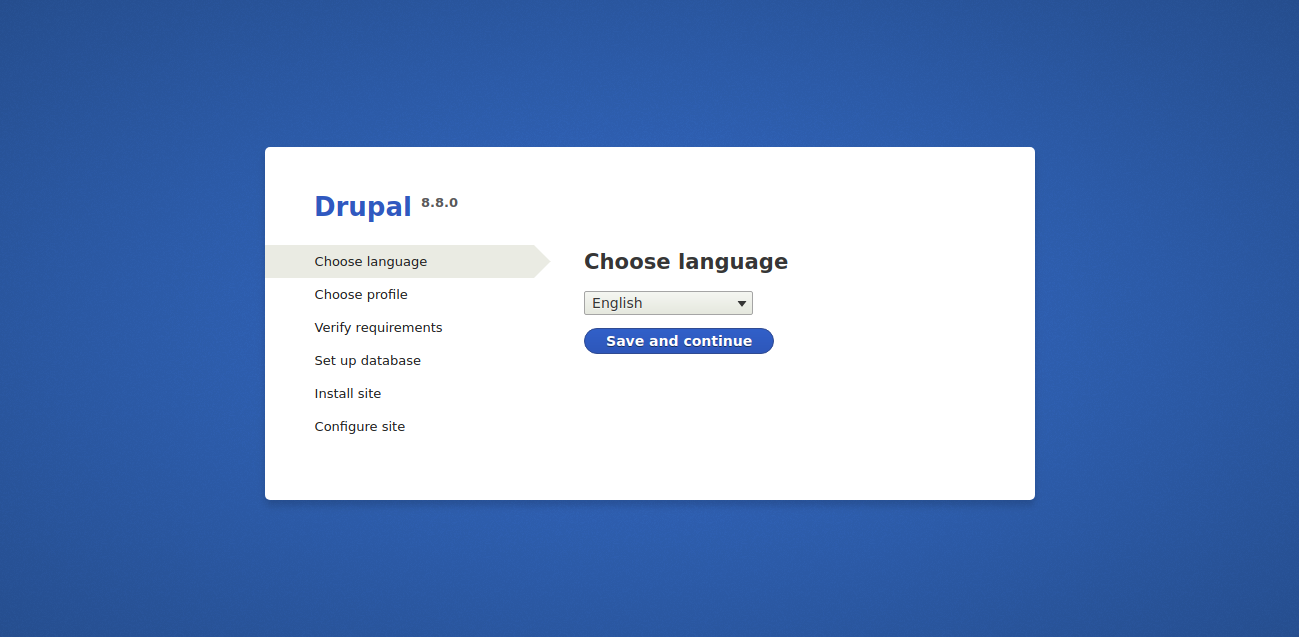
Access the Drupal installation wizard via http://your-server-ip.
Working with Docker Compose
Here are some common Docker Compose commands:
To stop the services:
docker-compose stop
Expected output:
Stopping drupal_drupal_1 ... done Stopping drupal_postgres_1 ... done
To start the services:
docker-compose start
To view logs of all containers:
docker-compose logs
To view logs of a specific container:
docker-compose logs drupal
To inspect the configuration file:
docker-compose config
To pause and unpause services:
docker-compose pause
Output:
Pausing drupal_postgres_1 ... done Pausing drupal_drupal_1 ... done
docker-compose unpause
Output:
Unpausing drupal_drupal_1 ... done Unpausing drupal_postgres_1 ... done
To remove services:
docker-compose down
Expected output:
Stopping drupal_drupal_1 ... done Stopping drupal_postgres_1 ... done Removing drupal_drupal_1 ... done Removing drupal_postgres_1 ... done Removing network drupal_default
To remove volumes:
docker-compose down --volumes
Expected output:
Removing network drupal_default WARNING: Network drupal_default not found. Removing volume drupal_drupal_modules Removing volume drupal_drupal_profiles Removing volume drupal_drupal_themes Removing volume drupal_drupal_sites Removing volume drupal_db_data
Conclusion
This tutorial provided you with the steps to install and use Docker Compose on a CentOS 8 server. You should now have a fundamental understanding of how to manage Docker containers using Docker Compose.
FAQ
- What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. - Why use Docker Compose?
Docker Compose simplifies the process of managing multiple containers by using a single YAML file and a single command to streamline deployment. - Can Docker Compose be used in production environments?
While it’s primarily designed for development and testing, Docker Compose can be adapted for production, but Docker Swarm or Kubernetes are more commonly used for production deployments. - How do I update Docker Compose?
You can update Docker Compose by downloading the latest binary from the official GitHub repository and replacing the existing one. - Is it necessary to use Docker Compose for single-container applications?
No, for single-container applications, Docker by itself is sufficient. Docker Compose is mainly advantageous when managing applications consisting of multiple containers.
