If you’re searching for a command-line utility to sort content within text files, look no further than Sort, a specialized tool for this task. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the Sort command using straightforward examples. Note that all examples have been tested on an Ubuntu 22.04 LTS system.
Linux Sort Command
The Sort command enables the sorting of lines in a text file. Below is its syntax:
sort [OPTION]... [FILE]...
The command’s man page defines it as follows:
Write sorted concatenation of all FILE(s) to standard output. With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Here are some Q&A-styled examples to help you understand how the sort command functions:
Q1. How to Use the Sort Command?
If you have a file with some names and want them sorted alphabetically, simply pass the filename to the Sort command.
Example:
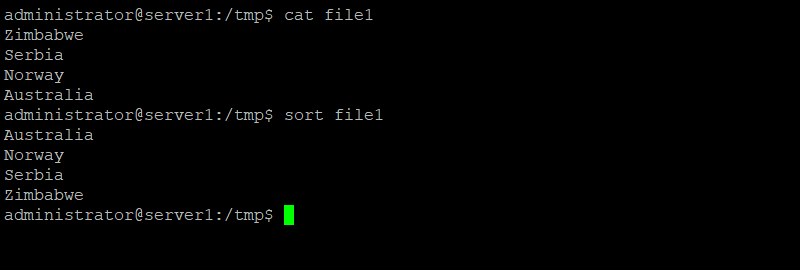
sort file1
If file1 contains the following lines:
Zimbabwe Serbia Norway Australia
The output will be:
Australia Norway Serbia Zimbabwe
Example image:
Q2. How to Make Sort Ignore Leading Blanks?
The output might appear unexpected when lines have leading blanks, depending on your locale. Consider this example:
If your file contains the following:
Zimbabwe Serbia Norway Australia
And you run the Sort command, you might see:
Norway Serbia Australia Zimbabwe
This occurs because lines with leading blanks are sorted by those blanks first. To ignore leading blanks, use the -b option. The output will then be:
Australia Norway Serbia Zimbabwe
Q3. How to Make Sort Ignore Case?
To ignore the case when sorting, use the -f option. Without this, lines starting with uppercase letters appear before those starting with lowercase.
Example:
sort -f file1
Q4. How to Make Sort Compare Numbers?
If your file contains numbers and you want to sort them numerically, use the -g option.
sort -g file1
Example input:
32000 2500 50000 54
Output:
54 2500 32000 50000
Q5. How to Make Sort Work with Human-Readable Numeric Values?
For sorting human-readable numeric values like 1K, 2G, use the -h option.
sort -h file1
Example input:
1M 2G 3K
Output:
3K 1M 2G
Q6. How to Make Sort Only Check for Sorted Input?
To verify if a file is sorted without sorting, use the -c option.
sort -c file1
Example file1 contents:
dhg lkh zyb abd
Output:
sort: file1:4: disorder: abd
This output indicates disorder and its location.
Q7. How to Merge Already Sorted Files with Sort?
To merge two pre-sorted files, utilize the -m option.
sort -m file1 file2
Example: If both file1 and file2 have the following:
abd dhg lkh zyb
Output with -m option:
abd abd dhg dhg lkh lkh zyb zyb
Q8. How to Save Sort Output to a File?
By default, the Sort command outputs to STDOUT. To save it to a file, use -o followed by the target filename.
Example:
sort file1 -o output.txt
Conclusion
The Sort command offers numerous options. We’ve covered a few essential ones here. Practice these, and then refer to the command’s man page for further details.
FAQ
What is the default sorting order in the Sort command?
The Sort command sorts text lines alphabetically by default.
Can I sort in reverse order?
Yes, use the -r option to sort in reverse order.
Does the Sort command modify the original files?
No, by default, Sort does not modify the original files. To save the sorted output to a file, use the -o option.
