Role-based access control (RBAC) is a crucial method for assigning access to computer or network resources within a Kubernetes cluster.
This article explores the fundamental concepts of RBAC and demonstrates how to create Role, ClusterRole, RoleBinding, and ClusterRoleBinding objects.
We will also walk through creating a kubeconfig file to provide limited access to a specific user within a chosen namespace.
Understanding RBAC Basics
- Role or ClusterRole contains a set of permissions.
- A Role defines permissions within a specific namespace, whereas a ClusterRole is a non-namespaced resource.
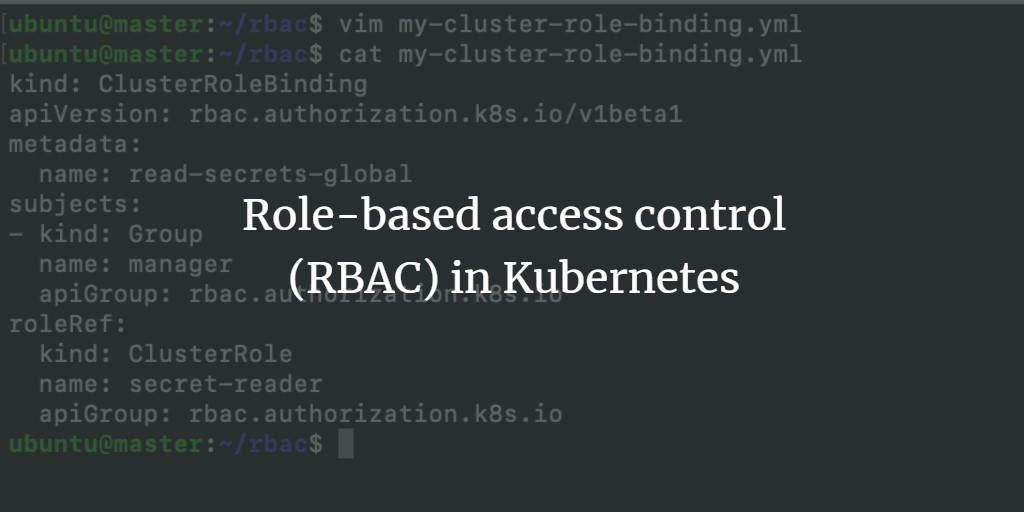
- A RoleBinding grants the permissions defined in a Role to a user or group of users. In contrast, a ClusterRoleBinding provides that access cluster-wide.
- A RoleBinding may reference any Role in the same namespace or a ClusterRole and bind it to the namespace of the RoleBinding.
- A kubeconfig file is used to configure access to Kubernetes through the kubectl command-line tool.
For a detailed understanding of RBAC, refer to the official Kubernetes documentation here.
Pre-requisites
- A Kubernetes Cluster with at least one worker node. If you need guidance to set up a Kubernetes cluster, click here. This guide helps create a Kubernetes cluster with one master and two nodes on AWS Ubuntu EC2 Instances.
Objectives
- Create Role, Role Binding, Cluster Role, and Cluster Role Binding object files.
- Deploy these RBAC objects within the cluster.
- Assign user access through the kubeconfig file.
- Summarize the creation process of the kubeconfig file.
Create Role, Role Binding, Cluster Role, and Cluster Role Binding Object Files
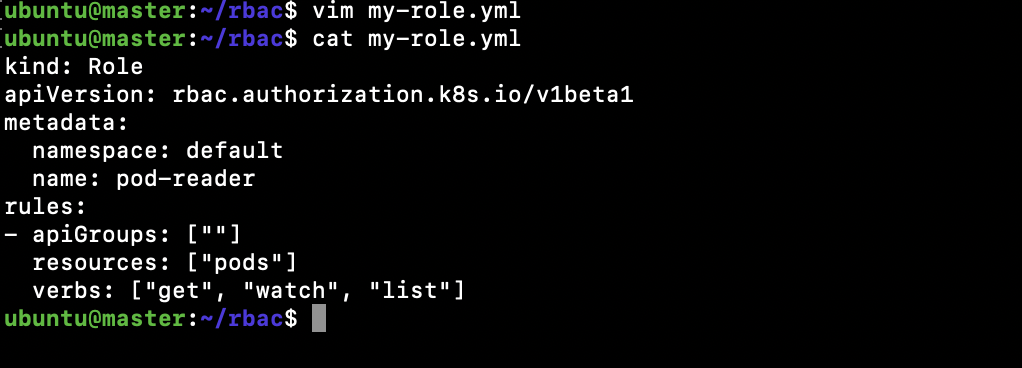
Create a file for a Role in the “default” namespace to grant get, watch, and list access to pods:
vim my-role.yml
kind: Role apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: namespace: default name: pod-reader rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods"] verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
…
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the fundamentals of Role, RoleBinding, and ClusterRole, ClusterRoleBinding and created these objects within our cluster. We also crafted a config file to enable a specific user to execute operations within a designated namespace. RBAC is an indispensable tool for managing access to a Kubernetes cluster.
FAQ
What is the difference between Role and ClusterRole in Kubernetes?
A Role applies permissions within a specific namespace, while a ClusterRole can apply permissions across the entire cluster.
How does a RoleBinding differ from a ClusterRoleBinding?
A RoleBinding assigns the permissions in a Role to a user or group within a single namespace. A ClusterRoleBinding does so across the entire cluster.
What is the purpose of a kubeconfig file?
A kubeconfig file configures access to Kubernetes clusters, allowing users to specify clusters, namespaces, and authentication mechanisms.
Can I use a ClusterRole in a RoleBinding?
Yes, a RoleBinding can reference a ClusterRole, thereby binding that ClusterRole to the namespace of the RoleBinding.